The UK financial system contracted within the second quarter, with households chopping spending as the price of dwelling disaster started to chew and well being sector output falling as Covid circumstances and testing declined.
Gross home product, the measure of the amount of products and providers produced, fell 0.1 per cent within the second quarter of the yr after rising 0.7 per cent within the earlier quarter.
A brief restoration is anticipated within the third quarter earlier than the UK slides into recession over the winter as additional rises in vitality costs squeeze family incomes and hit spending.
The decline was sharper on the finish of the quarter, with GDP falling 0.6 per cent in June, however this drop mirrored two misplaced work days from the Queen’s platinum jubilee. The Workplace for Nationwide Statistics, nevertheless, stated the celebrations had “little affect on the quarterly estimates” and the drop in GDP mirrored financial development grinding to a halt.
Total, the figures on Friday have been near these anticipated by economists and the Financial institution of England.
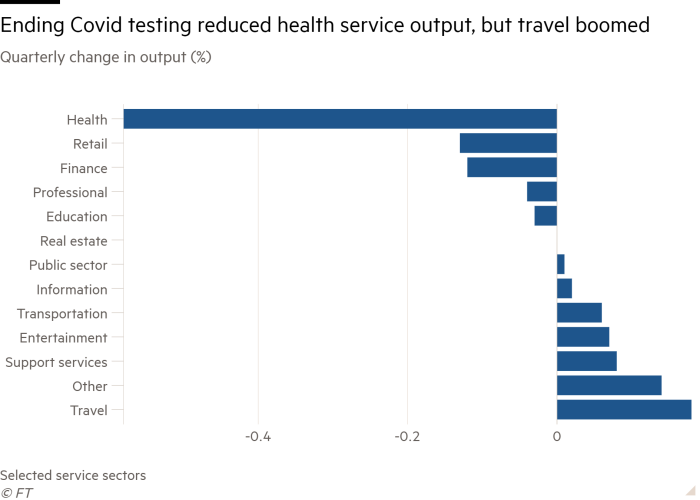
Darren Morgan, director of financial statistics on the ONS, stated the financial system “shrank barely” over the quarter with weak well being and retailing partially offset by “development in accommodations, bars, hairdressers and out of doors occasions throughout the quarter”.
Yael Selfin, chief UK economist at KPMG, stated the tip of the coronavirus take a look at and hint programme was vital within the second quarter decline in output and whereas this was momentary, weak spot could possibly be seen throughout the financial system.
“Households are already bruised by rising inflation, which is placing a squeeze on actual incomes, whereas rising rates of interest are making servicing mortgages much less reasonably priced. The anticipated rise in Ofgem’s utility tariff cap this autumn could possibly be the ultimate straw earlier than the UK enters a consumer-driven downturn,” she stated.
The UK financial system carried out higher than the US within the second quarter, however worse than the opposite G7 economies of Germany, France, Italy and Canada, which noticed better bouncebacks from the pandemic.
Nadhim Zahawi, the chancellor, stated: “I do know that instances are robust and folks shall be involved about rising costs and slowing development, and that’s why I’m decided to work with the Financial institution of England to get inflation underneath management and develop the financial system.”
Some economists have been extra gloomy and thought the decline in GDP already marked the beginning of a recession. Stephen Millard, deputy director of the Nationwide Institute of Financial and Social Analysis, stated: “It now appears just like the UK financial system entered a recession [because] we anticipate output to proceed falling over the subsequent three quarters.”

The main points of the second-quarter figures confirmed households already feeling the pinch, with consumption down 0.2 per cent, offset by some excellent news from enterprise funding, which rose 3.8 per cent. Enterprise funding has been erratic in latest quarters and was nonetheless 6 per cent decrease than pre-pandemic ranges.
Commerce efficiency was once more poor with one other report commerce deficit, excluding treasured metals. Exports have been £27.9bn decrease than imports on this measure, a niche representing 4.5 per cent of nationwide revenue, the very best since comparable information started in 1997.
A lot of this deficit displays imports of costly oil and gasoline, however there have additionally been notable will increase in imports of automobiles and equipment from the EU with out corresponding rises in exports.
On a sectoral foundation, the principle decline in output within the second quarter got here in providers, notably within the well being sector and in retailing, offset by enhancements in providers associated to the booming journey sector. Manufacturing contracted barely, as did the North Sea oil and gasoline sector regardless of report costs.
The figures present that the UK financial system was 0.6 per cent bigger than it was within the quarter instantly earlier than the pandemic, however considerably smaller than anticipated, suggesting lasting injury to financial efficiency.
















