by visualcapitalist
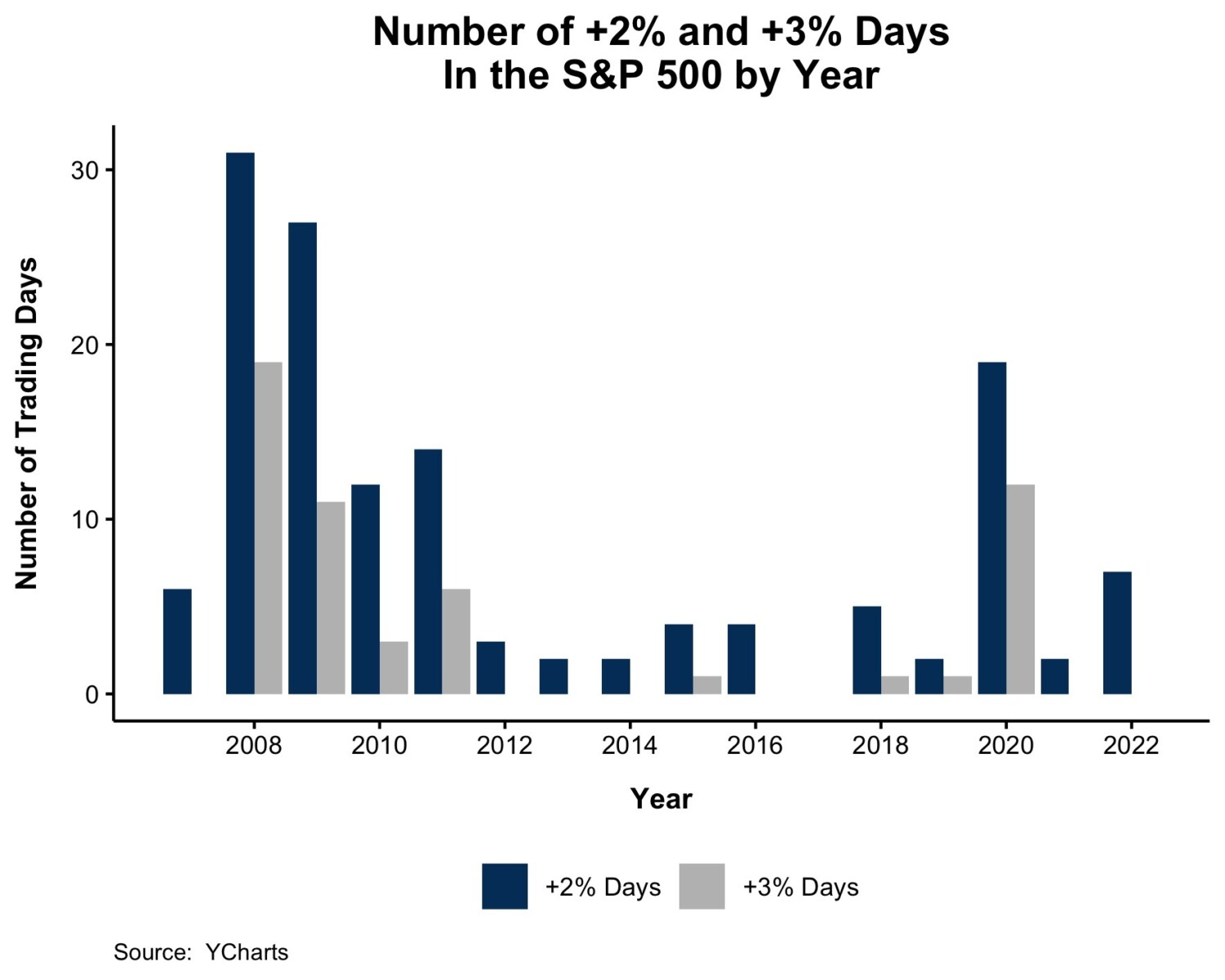
Based on the Federal Reserve (Fed), U.S. shopper debt is approaching a record-breaking $16 trillion. Critically, the speed of enhance in shopper debt for the fourth quarter of 2021 was additionally the best seen since 2007.
This graphic supplies context into the buyer debt scenario utilizing information from the tip of 2021.
Housing Vs. Non-Housing Debt
The next desk consists of the information used within the above graphic. Housing debt covers mortgages, whereas non-housing debt covers auto loans, pupil loans, and bank card balances.
Supply: Federal Reserve
Tendencies in Housing Debt
Dwelling costs have skilled upward strain because the starting of the COVID-19 pandemic. That is evidenced by the Case-Shiller U.S. Nationwide Dwelling Worth Index, which has elevated by 34% because the begin of the pandemic.
Driving this progress are varied pandemic-related impacts. For instance, the price of supplies similar to lumber have seen huge spikes. We’ve coated this story in a earlier graphic, which confirmed what number of properties might be constructed with $50,000 value of lumber. Usually, these larger prices are handed on to the buyer.
One other key issue right here is mortgage charges, which fell to all-time lows in 2020. When charges are low, customers are in a position to borrow in bigger portions. This will increase the demand for properties, which in flip inflates costs.
Finally, larger house costs translate to extra mortgage debt being incurred by households.
No Must Fear, Although
Economists imagine that right this moment’s housing debt isn’t a trigger for concern. It’s because the standard of debtors is way stronger than it was between 2003 and 2007, within the years main as much as the monetary disaster and subsequent housing crash.
Within the chart under, subprime debtors (these with a credit score rating of 620 and under) are represented by the red-shaded bars:
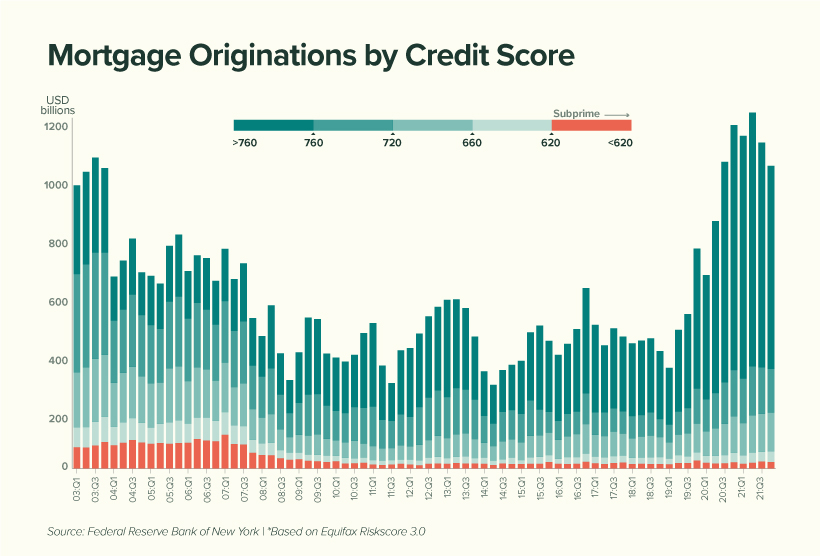
We will see that subprime debtors symbolize little or no (2%) of right this moment’s complete originations in comparison with the interval between 2003 to 2007 (12%). This means that American householders are, on common, much less prone to default on their mortgage.
Economists have additionally famous a decline within the family debt service ratio, which measures the share of disposable earnings that goes in direction of a mortgage. That is proven within the desk under, together with the common 30-year mounted mortgage price.
| 12 months | Mortgage Funds as a % of Disposable Earnings | Common 30-12 months Fastened Mortgage Charge |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 12.0% | 8.2% |
| 2004 | 12.2% | 5.4% |
| 2008 | 12.8% | 5.8% |
| 2012 | 9.8% | 3.9% |
| 2016 | 9.9% | 3.7% |
| 2020 | 9.4% | 3.5% |
| 2021 | 9.3% | 3.2% |
Supply: Federal Reserve
Whereas it’s true that People are much less burdened by their mortgages, we should acknowledge the lower in mortgage charges that occurred over the identical interval.
With the Fed now growing charges to calm inflation, People might see their mortgages start to eat up a bigger chunk of their paycheck. In truth, mortgage charges have already risen for seven consecutive weeks.
Tendencies in Non-Housing Client Debt
The important thing tales in non-housing shopper debt are pupil loans and auto loans.
The previous class of debt has grown considerably over the previous twenty years, with progress truly fizzling out through the pandemic. This may be attributed to COVID aid measures which have briefly lowered the rate of interest on direct federal pupil loans to 0%.
Moreover, these loans had been positioned into forbearance, that means 37 million debtors haven’t been required to make funds. As of April 2022, the worth of those waived funds has reached $195 billion.
Over the course of the pandemic, only a few direct federal debtors have made voluntary funds to cut back their mortgage principal. When funds finally resume, and the 0% rate of interest is reverted, economists imagine that delinquencies might rise considerably.
Auto loans, alternatively, are following the same trajectory as mortgages. Each new and used automobile costs have risen because of the world chip scarcity, which is hampering manufacturing throughout the complete trade.
To place this in numbers, the common worth of a brand new automobile has climbed from $35,600 in 2019, to over $47,000 right this moment. Over the same timeframe, the common worth of a used automobile has grown from $19,800, to over $28,000.
Assist Assist Unbiased Media, Please Donate or Subscribe:
Trending:
Views:
13