‘On-chain’1 crypto-asset transaction volumes have seen speedy development globally pushed by retail and institutional adoption, significantly because the starting of the Covid-19 pandemic and towards a backdrop of terribly free world monetary circumstances. The rising crypto-asset trade is various and gives completely different potential alternatives and dangers throughout several types of property. Whereas 1000’s of crypto property exist, bitcoin, ether, and a small set of stablecoins characterize the big majority of crypto volumes, with a comparatively minor however rising position for Decentralised Finance (DeFi) – an experimental monetary providers ecosystem that depends on a distributed ledger or related expertise.
In gentle of its rising scale, range, complexity, and interconnectedness with the regulated monetary system which can amplify dangers, understanding the primary drivers behind crypto-assets utilization is related for policymakers, customers, and trade alike.
Whereas bitcoin, the unique crypto asset, was conceived as a peer-to-peer digital money system with out the necessity for an middleman, crypto property, together with stablecoins, are at present not broadly used as a medium of change, though latest analysis finds proof that bitcoin has been used as a car for home transactions and worldwide funds (e.g. Graf von Luckner et al. 2021). Extra related elements for crypto-asset adoption may additionally embrace excessive anticipated returns from speculative funding (Auer and Tercero-Lucas 2021), their position as a perceived macro hedge defending towards macro-financial instability and extreme inflation regardless of their excessive volatility (Blau et al. 2021, Conlon et al. 2021), and regulatory arbitrage, significantly associated to illicit exercise. Given their ease of storage and portability, crypto property may additionally help individuals “dwelling underneath the specter of hurt by their households, individuals of their communities, or repressive governments” (Peirce 2021). Concerning DeFi, Harvey et al. (2021) conclude that it has potential to beat the inherent challenges of the standard monetary sector of centralised management, restricted entry, inefficiency, opacity, and lack of inter-operability.
In a brand new paper (Feyen et al. 2022), we doc the rise in on-chain crypto-asset exercise all over the world on the nation degree – transactions which can be immediately recorded on the distributed ledger that underpins a crypto-asset – and empirically examine the affiliation of crypto-asset volumes throughout international locations with key world and home macroeconomic drivers.
Fast rise of crypto exercise all over the world
Though knowledge gaps are important (e.g. IMF 2021), it seems that crypto-asset exercise is a worldwide phenomenon. Some trade estimates declare that 100-200 million individuals all over the world owned or use crypto property in 2021, together with in lots of rising market and growing economies (EMDEs).
We use a big world month-to-month nation panel of on-chain crypto-asset transaction volumes of worth despatched in US {dollars} offered by Chainalysis, a worldwide blockchain evaluation firm, to analyze the potential drivers of crypto-asset exercise in varied methods. The pattern spans the interval April 2019 to June 2021 and covers 174 international locations and 114 completely different crypto property. We mapped all crypto property into 4 teams: (1) Bitcoin, (2) Ethereum, (3) stablecoins,2 and (4) DeFi and others.3
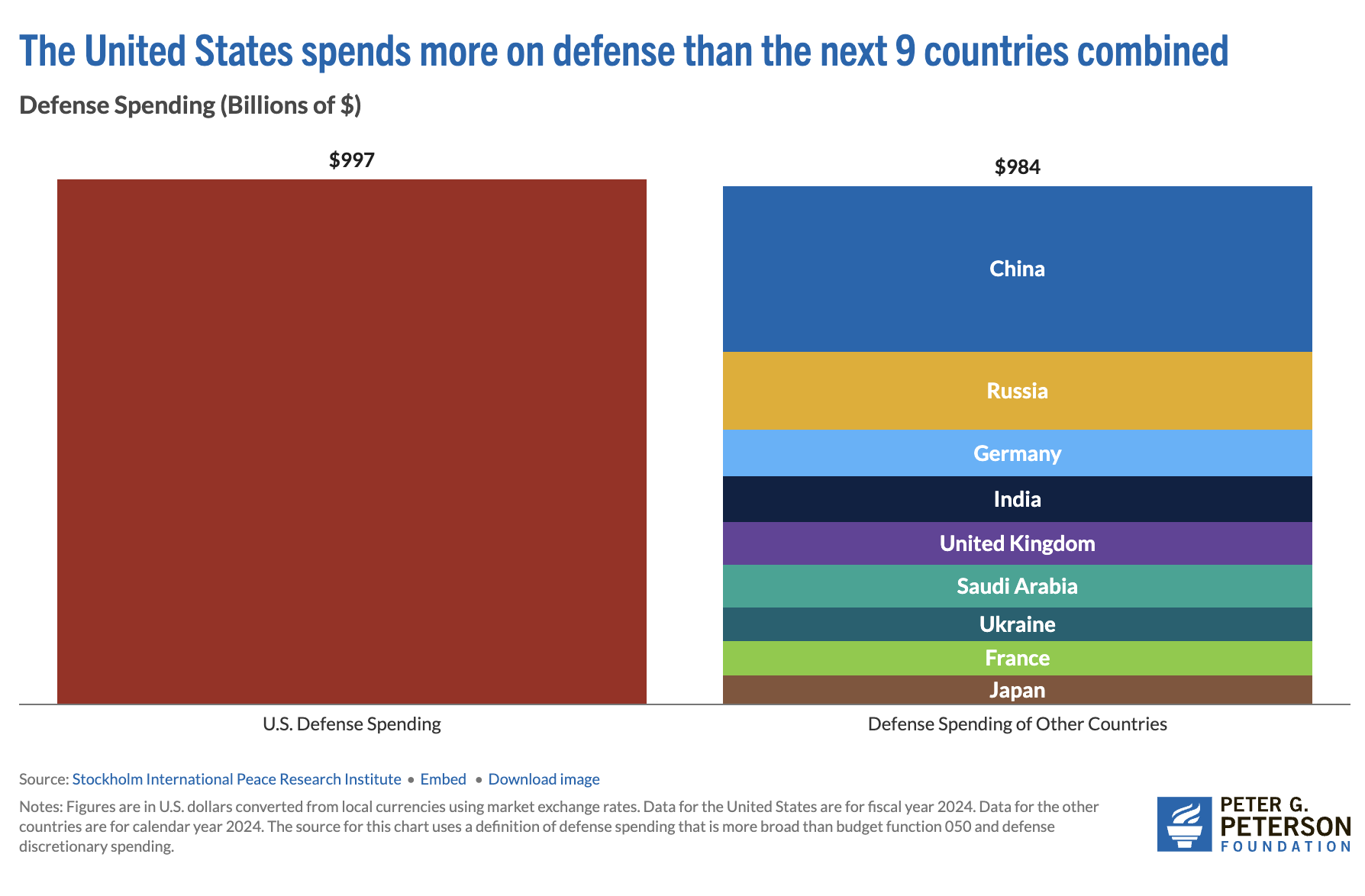
Complete crypto-asset on-chain quantity over the previous two years surged to a complete of $2.8 trillion within the first half of 2021 alone. Determine 1 illustrates that the volumes in ether (40%) and stablecoins (24%) has gained extra share over time in comparison with bitcoin (24%); DeFi and different crypto property characterize 12%. When crypto exercise by transaction dimension, we discover that enormous worth transfers ($2.68 trillion) dwarf smaller transaction dimension transfers ($128 billion), suggesting a disproportionately massive position of institutional exercise.
Determine 1 Complete crypto-asset quantity by asset sort (in US {dollars})
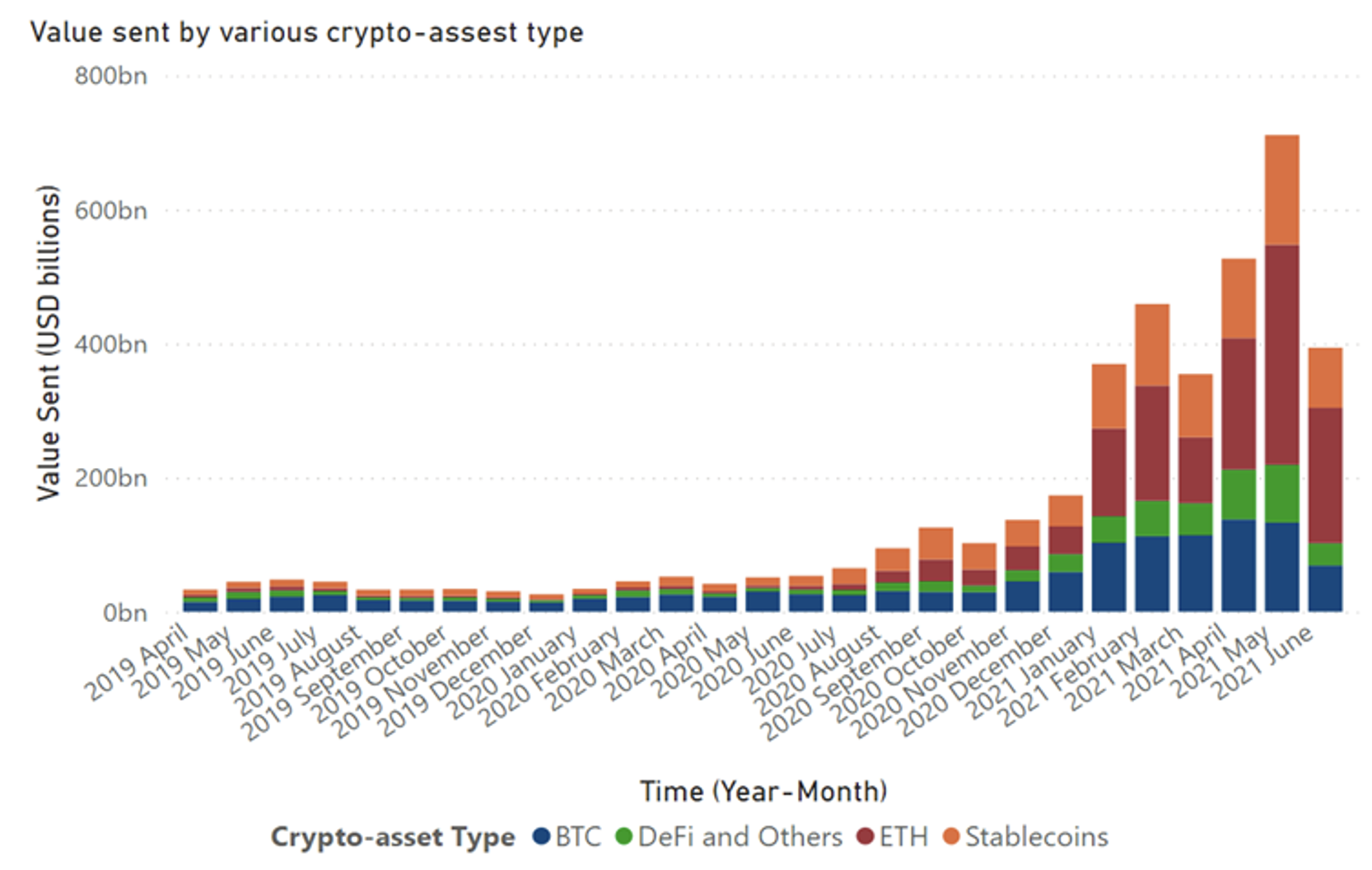
Sources: Chainalysis, World Financial institution employees calculations.
Determine 2 reveals that the geographical distribution of crypto-asset exercise is world. Annualised complete volumes of crypto-asset exercise for 2021 relative to GDP have turn out to be noticeable, significantly in areas like Latin America and the Caribbean (median: 0.07% of GDP), sub-Saharan Africa (median: 0.06% of GDP) and Europe and Central Asia (median: 0.10% of GDP). Exercise is comparatively restricted in lower- and middle-income international locations and is dominated by bitcoin and ether. Smaller transactions nonetheless characterize a minor fraction (10%) of complete volumes throughout international locations. The share of stablecoins additionally stays comparatively low with 16% of the general quantity.
Determine 2 Complete crypto-assets quantity by asset sort(April 2019-June 2021)
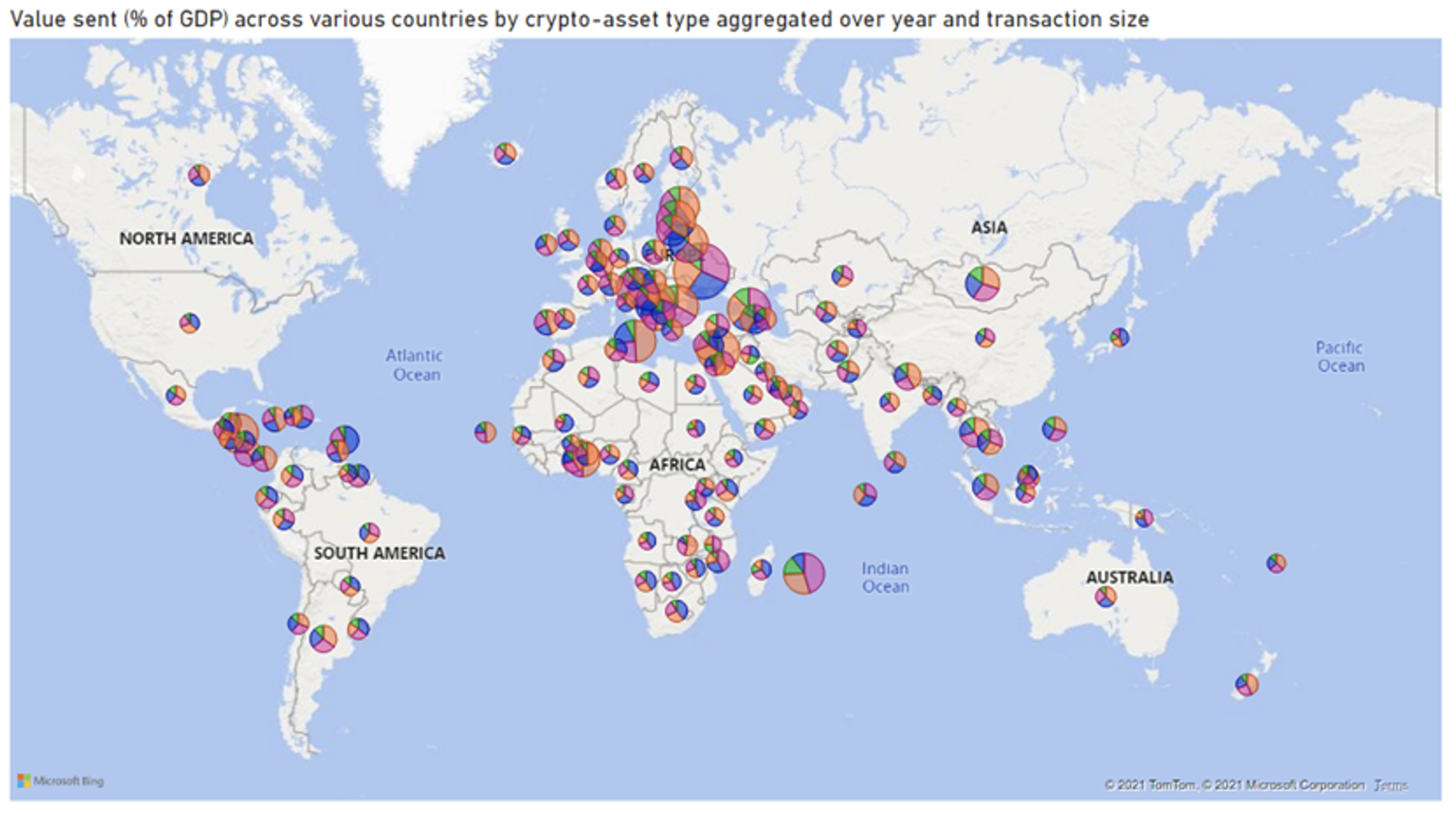
Supply: Chainalysis, World Financial institution employees calculations.
Notice: A map of crypto-assets exercise scaled by a rustic’s GDP – bigger bubbles point out greater exercise relative to the dimensions of the financial system. The bubble sizes representing the relative values despatched (% of GDP).
The information additionally counsel that almost all of the quantity is concentrated in North America (the US particularly) and Europe and Central Asia, with these two areas mixed representing 56% of total exercise aggregated over our full pattern interval. Whereas developed and high-income economies proceed to characterize a bigger share of the general crypto exercise in absolute worth of transfers throughout all transaction sizes, the share of exercise in areas like East Asia Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, South Asia, and Sub-Saharan Africa is gaining momentum.
Macro-financial drivers of crypto-asset exercise
The empirical findings counsel that crypto-asset volumes are strongly related to a set of forward-looking world macro-financial elements – which can in the end form home macro-financial circumstances – quite than latest home macroeconomic developments. For instance, controlling for a variety of worldwide and home elements, a ten basis-point improve in month-to-month US inflation expectations (on a five-year, five-year ahead foundation as embedded in US Treasury yields) will increase month-to-month crypto volumes by about 28 foundation factors. In distinction, country-level macroeconomic indicators (e.g. inflation and the change price) don’t seem like strongly associated with country-level volumes.
Nation-level volumes additionally transfer in the wrong way to gold costs, suggesting that crypto property are seen to some extent as an alternative choice to gold – a conventional world inflation hedge. The outcomes additional indicate that crypto property are perceived as a speculative ‘risk-on’ asset class, with greater volumes when actual US Treasury yields – a proxy for world monetary circumstances – are decrease. Crypto volumes additionally seem like supported by a momentum impact in crypto-asset costs additional suggesting that speculative motives play a job.
We additionally discover some tentative proof that crypto exercise is greater in international locations with greater info and communications expertise (ICT) penetration and broadband subscriptions per capita. This gives some help for the concept crypto property could tackle among the challenges related to cross-border funds, which may be sluggish and dear, however additional analysis is critical to substantiate this. Nascent implementations of latest applied sciences (e.g. the Lightning Community; see Poon and Dryja 2016) that might tackle present transaction throughput challenges of crypto property could assist speed up adoption for (cross-border) fee transactions, however these applied sciences are largely untested at scale and may additionally pose new dangers.
Conclusion
Crypto property are more and more considered an rising and various asset class as financial capabilities and dangers differ throughout crypto property (e.g. unbacked crypto property, stablecoins, and Decentralised Finance).
Whereas not a panacea to beat monetary sector challenges, crypto property and the underlying expertise maintain promise for monetary innovation, inclusion, effectivity, transparency, and capital formation. Nevertheless, in view of their decentralised and cross-border nature, which poses worldwide regulatory arbitrage challenges, crypto-assets additionally current a number of severe dangers, together with to monetary integrity, client and investor safety, truthful competitors, financial sovereignty, capital management enforcement, and taxation (e.g. FATF 2021, BCBS 2020, G7 2019). Additional, whereas crypto property nonetheless represent a small portion of the worldwide monetary system, they may in the end pose dangers to world monetary stability (e.g. FSB 2022).
Our findings shine new gentle on the speedy development and various drivers behind crypto-asset exercise and supply help to the notions that crypto property are perceived as a threat asset, a possible longer-term macro hedge, and a possible instrument to help cross-border funds. Nevertheless, our outcomes needs to be interpreted with warning: a good portion of the pattern interval contains extraordinary free world monetary circumstances; the crypto quantity knowledge have a brief historical past, depend on necessary limiting assumptions, and don’t characterize all crypto exercise; and crypto-assets characterize a fast-evolving, more and more various asset class and trade.
References
Auer, R and D Tercero-Lucas (2021), “Mistrust versus hypothesis? The drivers of cryptocurrency investments”, VoxEU.org, 6 October 2021
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) (2021), “Consultative Doc: Prudential Remedy of Cryptoasset Exposures”.
Blau, B, T Griffith and R Whitby (2021), “Inflation and Bitcoin: A Descriptive Time-Collection Evaluation”, Economics Letters 203.
Conlon, T, S Corbet and R McGee (2021), “Inflation and cryptocurrencies revisited: A Time-scale Evaluation”, Economics Letters 206.
Feyen, E, Y Kawashima and R Mittal (2022), “Crypto-assets exercise all over the world: Evolution and macro-financial drivers”, World Financial institution Working Paper.
Monetary Motion Process Power (FATF) (2021), “Up to date Steering for a Danger-Based mostly Method to Digital Belongings and Digital Asset Service Suppliers”.
Monetary Stability Board (FSB) (2022), “Evaluation of Dangers to Monetary Stability from Crypto-assets”.
G7 Working Group on Stablecoins (2019), “Investigating the Influence of International Stablecoins”.
Graf von Luckner, C, C Reinhart and Ok Rogoff (2021), “Decrypting New Age Worldwide Capital Flows”, NBER Working Paper 29337.
Harvey, C R, A Ramachandran and J Santoro (2021), DeFi and the Way forward for Finance, John Wiley & Sons.
Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF) (2021), “The Crypto Ecosystem and Monetary Stability Challenges”, Chapter 2 in International Monetary Stability Report.
Peirce, H (2021), “Paper, Plastic, Peer-to-Peer”, U.S. SEC Commissioner Remarks on the British Blockchain Affiliation’s Convention “Success By means of Synergy: Subsequent era Management for Extraordinary Instances”.
Poon, J and T Dryja (2016), “The Bitcoin Lightning Community: Scalable Off-Chain On the spot Funds”, Digital Foreign money Initiative paper, MIT Media Lab.
Endnotes
1 Not all crypto-assets transactions are ‘on chain’. ‘Off-chain’ transactions are solely recorded on centralised ledgers and personal order books of intermediaries corresponding to crypto-assets exchanges, custodial wallets, and monetary establishments. These ‘off-chain’ transactions could contain shopping for or promoting of crypto-assets in change for fiat foreign money or exchanging one crypto-asset for an additional.
2 The stablecoin class in our evaluation embrace among the main US dollar-linked stablecoins: USD Coin (USDC), Tether (USDT), DAI (crypto-assets backed), TrueUSD (TUSD), Paxos USD (Greenback (PAX), Binance USD (BUSD), and Gemini Greenback (GUSD). In November 2021, the highest three stablecoins accounted for about 85% of the full stablecoin market capitalisation.
3 The ‘DeFi and Others’ class contains 103 completely different crypto property. The highest ten with the biggest quantity are: Wrapped Ether (WETH), XRP, Litecoin (LTC), Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), Chainlink (LINK), Bitcoin Money (BCH), EOS, Uniswap (UNI), Yearn Finance (YFI), and Sushiswap (SUSHI).