Surviving the Conquest: Inter-ethnic complementarities and indigenous resilience to pandemics and struggle in Mexico
Each struggle and pandemic have disrupted right now’s international commerce networks, imposing a disproportionate burden on particular nations and totally different ethnic teams with them. Such differential results of a worldwide pandemic resonate with some of the traumatic moments in human historical past, the Conquest of Mexico. In its aftermath, confronted by the ‘germs and metal’ of the conquistadores (Diamond 1997), tens of millions of indigenous individuals died. However as we present, the catastrophe was removed from indiscriminate. Who survived and why?
Utilizing a wealthy set of main sources, together with Aztec tribute rolls and early sixteenth century censuses, we reconstruct the destiny of 1,093 indigenous settlements (altepetl) that existed within the historic core of Mexico. Determine 1 reveals hanging patterns each of entire communities annihilated by the top of the colonial interval, but in addition of indigenous resilience. Not like in Western Europe, the place the opening of commerce to the New World introduced rising populations to port cities (Acemoglu et al. 2005), their coastal counterparts in Mexico have been decimated. Within the central highlands, in distinction, the destiny of settlements was extra blended. General, the typical indigenous settlement inhabitants fell from 2,377 in 1548 to 128 by 1646. By 1790, 36% had disappeared totally; but 13% ended the colonial period bigger than they started. What accounts for these patterns?
Determine 1 Inhabitants change within the historic core of Mexico, 1548-1790
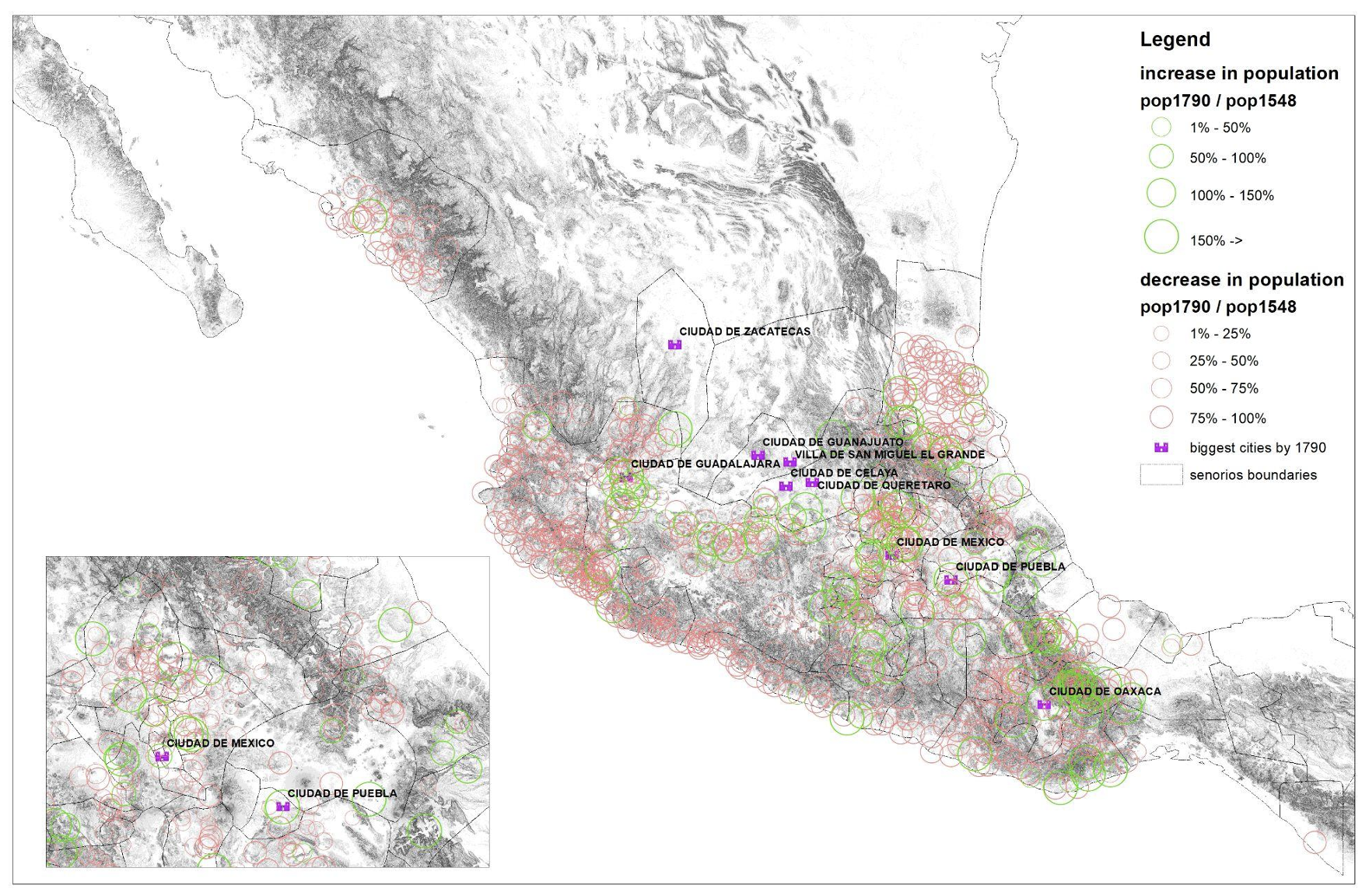
Supply: Diaz-Cayeros et al. (2022), primarily based upon the Suma de Visitas, and the Tanck de Estrada 2005
Two theories at the moment prevail for the inhabitants collapse. The ‘virgin soil’ speculation (Crosby 2003) blames novel pathogens that reached pandemic proportions among the many beforehand unexposed indigenous inhabitants. In distinction, the ‘black legend’, following up to date observer Fra Bartolome de las Casas, blames the ruthless exploitation of the native inhabitants by European settlers.
Combining financial concept, trendy epidemiological fashions and novel disaggregated knowledge permits us to shed new gentle on these questions. We draw upon a easy theoretical framework (outlined in Jha 2018) that considers the situations that help peaceable coexistence equilibria amongst totally different ethnic teams dwelling in the identical location.
When contemplating how commerce between nations can help peace, comparative benefits are sometimes assumed (Polachek and Sieglie 2007) and the presence of other buying and selling companions might be essential (Martin et al. 2008). When people stay in the identical place, and thus share many endowments, nevertheless, sustaining inter-group commerce might be much more fragile: alternatives usually emerge to violently seize or, over very long time durations, replicate each other’s manufacturing processes. This fragility of the positive aspects from commerce is accentuated when one group is militarily susceptible, equivalent to is commonly the case for minority ethnic teams. Below what situations then can market alternate help peaceable coexistence and prosperity for susceptible teams over time?
Jha (2018) distinguishes between susceptible indigenous teams, for whom leaving a specific location is comparatively expensive, and susceptible outsider teams, equivalent to intermediary minorities, who’re extra cellular. He considers a setting the place, each interval, people can select to depart, to provide a great, and to focus on one other with violence to grab their earnings. The paper reveals that, on this surroundings, a set of situations grow to be essential for supporting equilibria with ethnically blended populations and no violence over lengthy horizons. The primary is that members of various teams are capable of preserve financial actions that complement, fairly than compete with, each other. Additional, the supply of complementarity for susceptible group members must be very expensive to expropriate and replicate. That is usually the case for middlemen minorities, equivalent to Muslims in medieval Indian Ocean ports, whose complementarity stems from entry to exterior buying and selling networks. Buying and selling networks are intangible, thus unimaginable to expropriate, and when large-scale equivalent to as a result of Hajj, grow to be tough to duplicate.
However past this, over very long time horizons, susceptible group members want to have the ability to credibly threaten to withhold their complementary manufacturing with a view to deter expropriative violence. Jha (2018) describes how, when their outdoors choices are good, equivalent to happens with falls in limitations to immigration elsewhere, susceptible outsiders that loved sturdy complementarities, equivalent to buying and selling minorities in Indian Ocean ports, Europe and elsewhere, have been capable of deter acquisitive dictators and others by threatening to depart and deny future commerce. Nonetheless, when the prices of leaving the place excessive, these communities have been extra more likely to see waves of pogroms as a substitute (Jha 2013, 2018).
Conquest-era Mexico exemplifies a good more durable surroundings for sustaining peace and prosperity for the susceptible. Indigenous communities, whose data, endowments, and networks are also concentrated regionally, usually discover it much more expensive to depart a particular location, not much less. With nowhere to go, even when indigenous teams produce a helpful good, they’re prone to being expropriated and coerced into its manufacturing via the specter of violence. To have the ability to withhold manufacturing and deter violence, subsequently, their effort must be tough to watch and subsequently coerce (Diaz-Cayeros and Jha 2017, Jha 2018). In our new paper (Diaz-Cayeros et al. 2022), we verify that the extent to which this was true performed essential roles in shaping the resilience of indigenous peoples within the Americas after the Conquest.
Our findings recommend that fairly than dealing with indiscriminate dying from illness and coercive violence, indigenous communities have been extremely resilient once they might produce items that embedded indigenous knowhow and ability that have been onerous to transplant elsewhere and in addition prized on worldwide markets. A key instance was cochineal, an indigenously domesticated insect that was additionally the best-known supply of pink dye till the event of synthetics within the Eighties (Baskes 2000, Diaz-Cayeros and Jha 2017). Extremely fragile, cochineal manufacturing required sturdy incentives, particular micro-climates, and particular strategies to maintain the bugs alive. Troublesome to watch and to transplant, it might stay an indigenous exercise regardless of turning into probably the most helpful processed good exported from New Spain (Baskes 2000, Diaz-Cayeros and Jha 2017). We distinction cochineal-producing settlements to these producing different internationally valued items. Cacao, the drink of Aztec nobles, was additionally native to Mexico however simply planted and replicated elsewhere. Gold and silver manufacturing may very well be monitored and coerced. Equally, we observe the destiny of settlements that produced artisanal items, equivalent to quetzal feathers, extremely valued by the Aztec court docket, however dismissed by the conquering Spanish.
Determine 2 Pre-Conquest settlements producing cochineal, cacao, gold, maize and different commodities
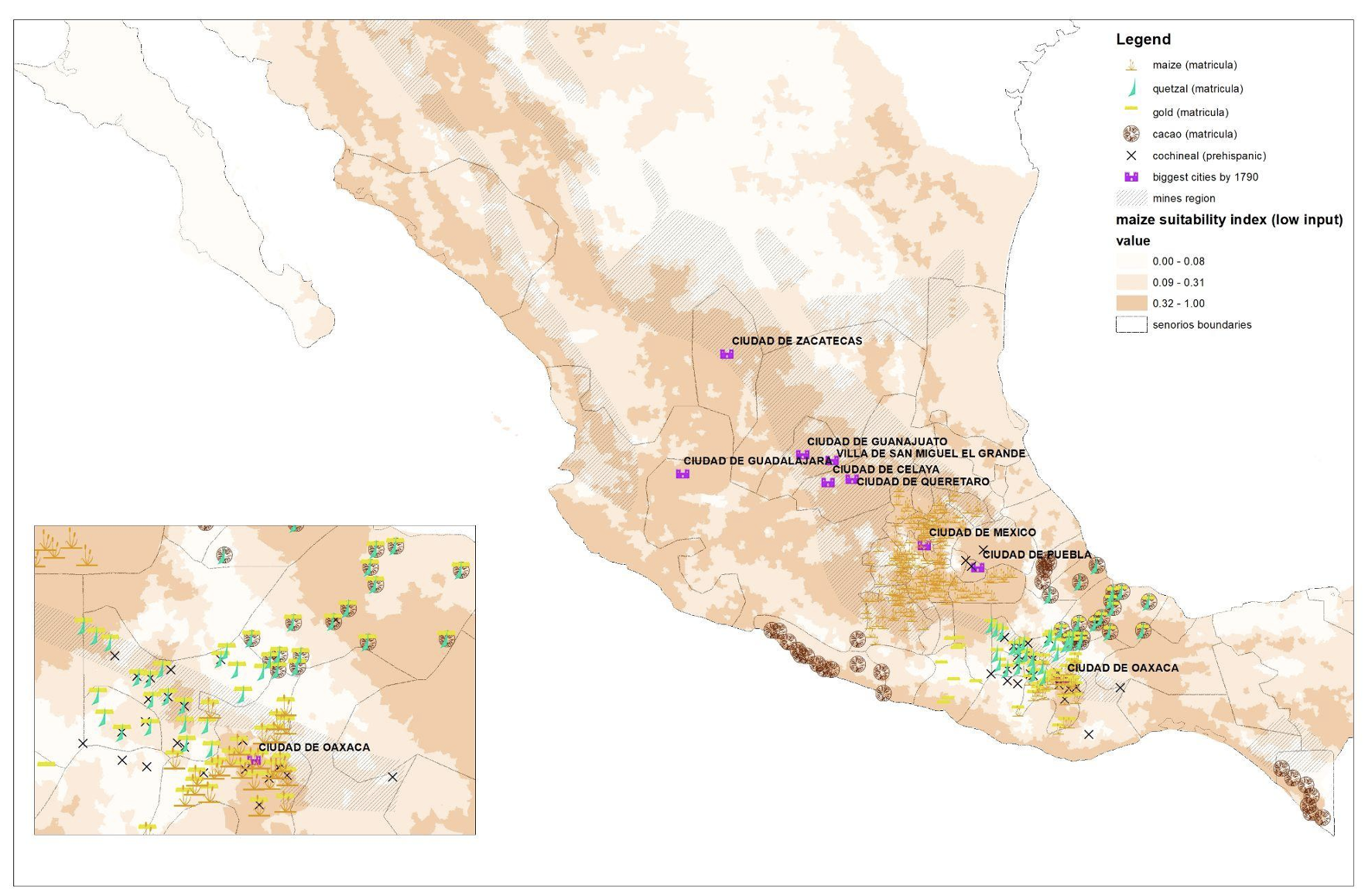
Supply: Diaz-Cayeros et al. (2022), primarily based upon the Codex Mendoza and different Conquest-era sources.
To reconstruct Conquest-era Mexico, we exploit two distinctive historic paperwork. The Codex Mendoza, mentioned to have been given by the final Aztec Emperor, Moctezuma, to Cortes himself on the time of the Conquest, particulars the tribute that totally different settlements owed to Tenochtitlan. We use this not solely to find out which pre-Conquest settlements produced cochineal and different commodities (Determine 2), but in addition to develop a prediction of pre-Columbian market entry and street networks. The Suma de Visitas (1548) enumerated the households in numerous components of newly- conquered Mexico, primarily based upon the ‘visits’ of clerical officers (Determine 3).
Determine 3 Reconstruction of Mexican inhabitants and market entry, 1548
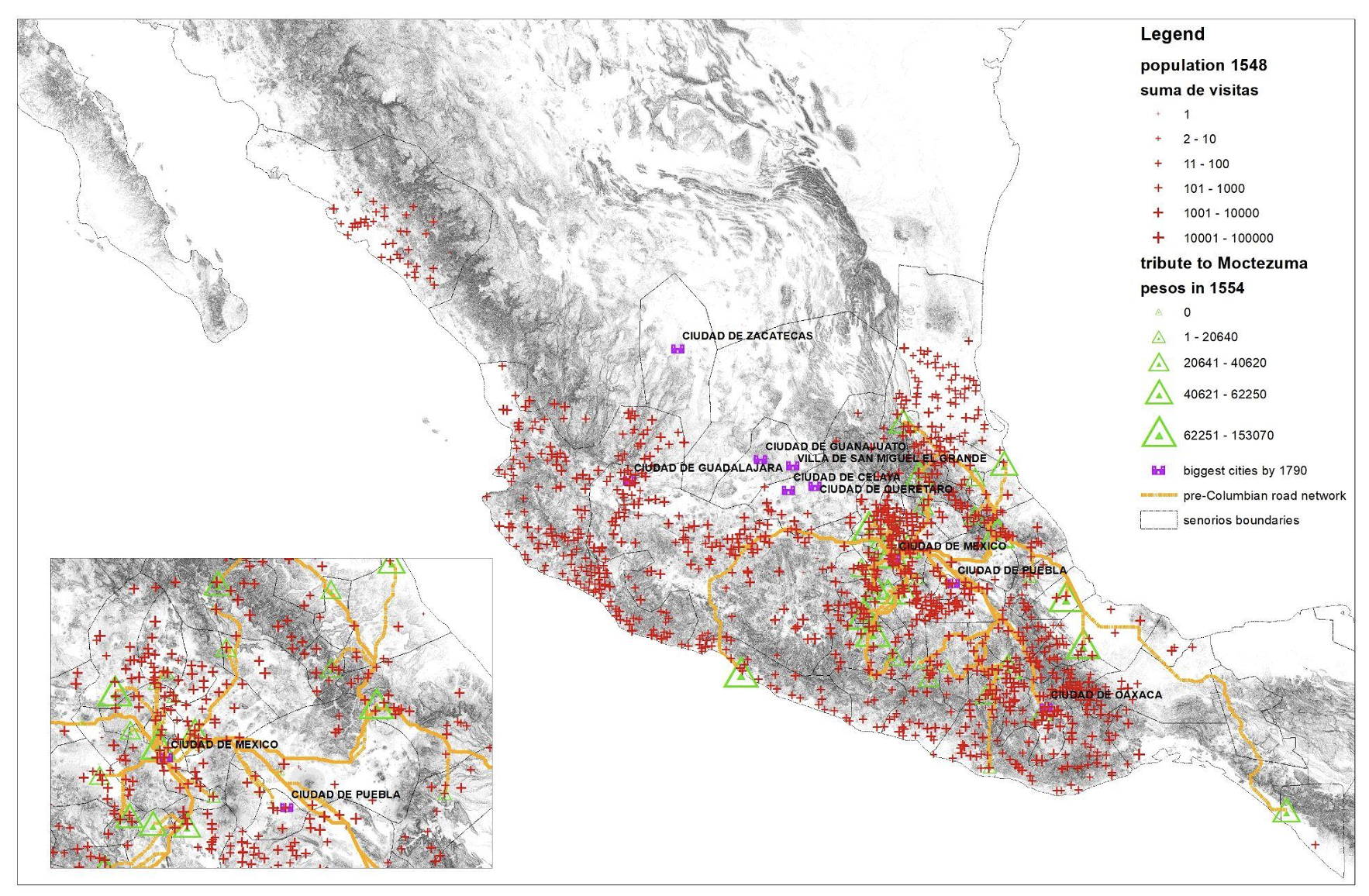
Supply: Diaz-Cayeros et al. (2022).
We use subsequent censuses and inhabitants counts all through the colonial interval to evaluate settlement survival. Determine 4 summarises these findings. The graph presents Kaplan-Meier survival capabilities, evaluating the share of settlements surviving over the colonial interval that specialised in numerous merchandise within the pre-Columbian interval. Observe that even on this uncooked comparability, cochineal-producing settlements are more likely to outlive all through the colonial interval.
Determine 4 Kaplan-Meier plots of the proportion of the survival of indigenous settlements producing totally different commodities relative to others, 1548-1790
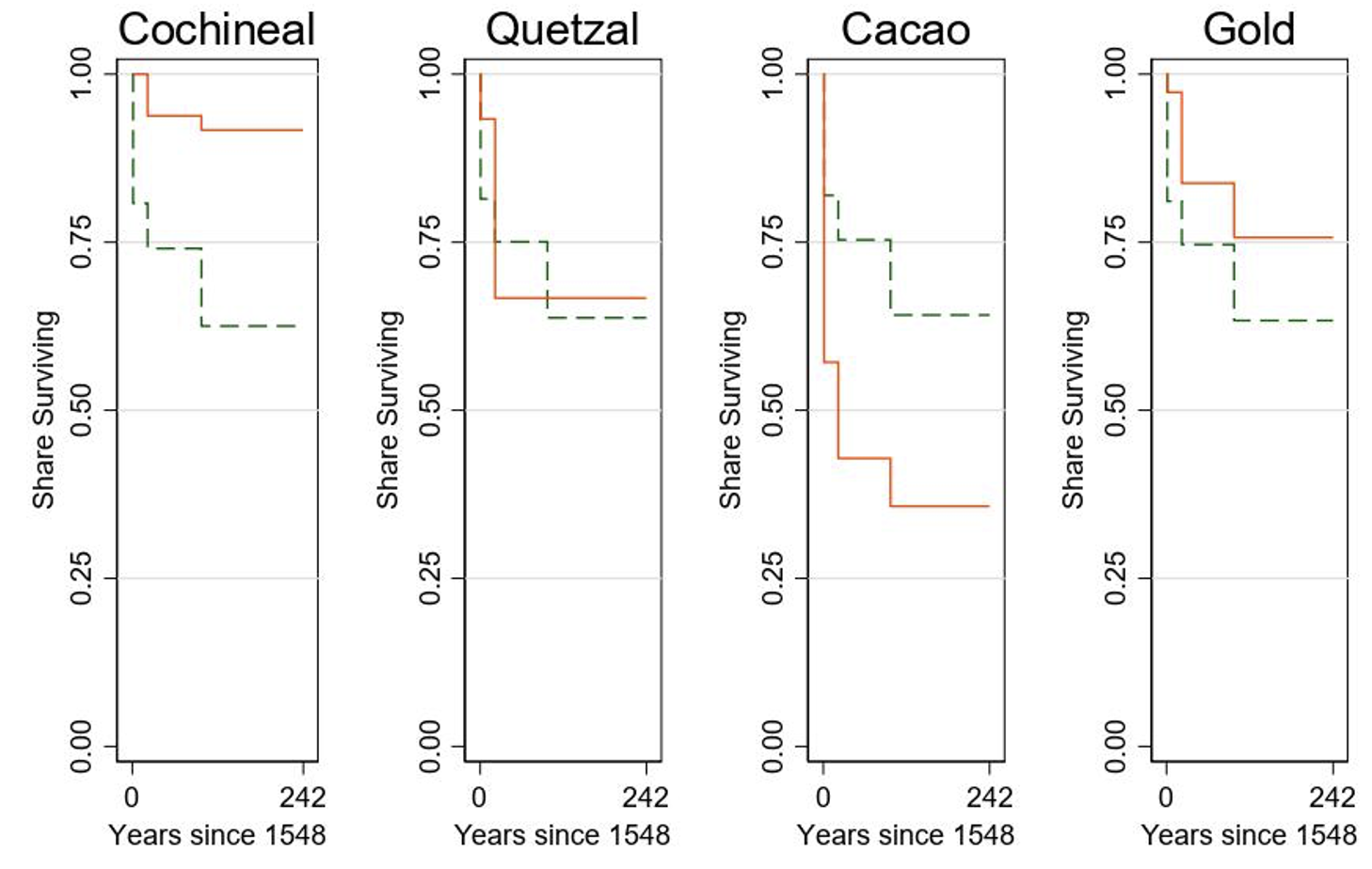
The variations show to be sturdy to tighter statistical comparisons. In comparison with different settlements with related preliminary populations, weather conditions, and exogenous illness propensities, we discover that indigenous settlements that produced cochineal on the time of the Conquest have been at 5 occasions decrease danger of disappearing annually throughout the colonial interval, have been 13 share factors extra more likely to live on in 1790, and loved populations 1.7 occasions bigger on the finish of the colonial interval. These patterns are sturdy to evaluating Altepeme with related imperial conquest histories and pre-Columbian market entry, evaluating inside the identical province or lordship, or accounting for spatial auto-correlation utilizing a spectral GMM regression. The findings will not be pushed by the selection Spanish colonists made to find and settle specifically locations. These variations are additionally sturdy to controlling for the propensity for the pandemic ailments predicted by trendy epidemiological fashions of the climatic envelopes for typhus, plague, dengue, and totally different candidates for the extra mysterious cocoliztli.
In distinction, settlements producing cacao (transplantable elsewhere) and gold (whose labour may very well be coerced) earlier than the Conquest, whereas each surviving twice so long as in any other case related settlements within the data, present no inhabitants benefits by the top of the colonial interval. Producers of quetzal feathers for the Aztec court docket, as soon as a prized commodity, noticed the best declines: quetzal-producing settlements have been 5 to 6 occasions much less more likely to survive the colonial period, and their common inhabitants was 86% smaller by 1790. Thus, susceptible communities’ capability to regulate to the specter of violence and illness depended critically on whether or not their abilities and endowments in the mean time of the Conquest positioned them to learn from autonomy fairly than subjugation.
The Mexican coastal areas, as soon as flourishing areas of indigenous settlement, are an necessary instance. Probably with a lot to realize from the brand new intercontinental trades, indigenous settlements on the coasts lacked sturdy inter-ethnic complementarities. As a substitute, these settlements have been well-suited for (replicable) cacao manufacturing, and inclined to typhus. Many communities could be worn out totally, partly by illness and partly from the rampages of the Conquistador Nuño de Guzman, who sought to coerce and enslave them. Elsewhere, the place cochineal was cultivated, encomenderos realised the advantages of giving the indigenous autonomy, as a substitute of forcing their labour. Such autonomy seems to have allowed the indigenous to raised reply to the illness environments they confronted, as epidemics have been a daily prevalence in pre-Columbian America. Mexican populations and politics would flip away from the ocean and commerce, and be decided by contests over land ever since.
The results of struggle and pandemics have been removed from uniform, as a result of some susceptible teams might train company of their quest for survival, whereas others have been hindered from doing so. Thus, it was human financial, social, and political responses that mediated the affect of pathogens on human beings.
References
Acemoglu, D, S Johnson and J Robinson (2005), “The Rise of Europe: Atlantic Commerce, Institutional Change, and Financial Development,” American Financial Evaluate 95(3): 546-579.
Baskes, J (2000), Indian retailers and markets, Stanford College Press.
Crosby, A W (2003), The Columbian alternate: organic and cultural penalties of 1492, Vol. 2, Greenwood Publishing Group.
Diamond, J (1997), Weapons, Germs and Metal: The Fates of Human Societies, W.W. Norton.
Diaz-Cayeros, A and S Jha (2017), “Conquered however not Vanquished: Complementarities and Indigenous Entrepreneurs within the Shadow of Violence’,” Technical Report.
Diaz-Cayeros, A, J Espinosa-Balbuena and S Jha (2022), “Pandemic Spikes and Damaged Spears: Indigenous Resilience after the Conquest of Mexico,” Journal of Historic Political Financial system 2: 89–133.
Jha, S (2013), “Commerce, establishments and ethnic tolerance: proof from South Asia,” American Political Science Evaluate.
Jha, S (2018), “Buying and selling for Peace,” Financial Coverage 33(95): 485–526.
Martin, P, T Mayer and M Thoenig (2008), “Make Commerce Not Conflict?”, Evaluate of Financial Research 75(3): 2008
Polachek, S and C Sieglie (2007), “Commerce, Peace and Democracy: An Evaluation of Dyadic Dispute”, in Okay Hartley and T Sandler (eds), Handbook of Defence Economics.