Monty Rakusen/DigitalVision through Getty Photographs
By Jan Frederik Slijkerman
The EU telecom business wants extra meat on the bones
It is no secret that a number of European sectors are presently going through a bunch of particular person challenges and collective headwinds – and the telecom sector is not any exception. The European Fee’s long-awaited report on European competitiveness – steered by former president of the European Central Financial institution, Mario Draghi – sheds mild on the intricacies of these challenges. Over time, European telecom firms have accepted a decrease creditworthiness, primarily on account of competitors coverage put in place to attain decrease client costs.
However whereas decrease credit score rankings had been typically acceptable in an ultra-low rate of interest atmosphere, funding prices are actually transferring up, and we predict it is time for some firms to pay nearer consideration to their money movement profiles.
On this article, we delve into why and the way higher-rated telecom operators are higher positioned to face up to dangers from competitors and better pursuits than high-yield firms with decrease credit score rankings.
We have not too long ago witnessed extreme monetary stress at Altice France, whereas Italy and Denmark have misplaced their incumbent, built-in telecom operators. Telecom Italia (OTCPK:TIIAY, OTCPK:TIAIY) , as an example, has been damaged up right into a community firm and a consumer-facing companies enterprise. We additionally noticed this in Denmark a few years in the past. Telefonica (TEF) is one other firm additionally susceptible to being damaged up within the coming decade, whereas firms within the UK want higher money flows to have the ability to speed up investments. For instance, we anticipate that clearance of the Vodafone-Three merger will support investments within the UK. It is also fascinating to notice that BT has a comparatively weak money movement profile, whereas TalkTalk’s monetary misery is an extra testomony to the competitiveness of the UK market. In brief, extra leverage comes at a price – which Altice France and TalkTalk are actually discovering out.
Robust competitors decreased the well being of telecom firms
Through the years, we’ve got witnessed sturdy competitors in European telecom markets, pushed by regulation. However whereas sturdy competitors legal guidelines efficiently lowered client costs, additionally they had a detrimental impact on the profitability of some firms. We offer examples of steep, annual declines in profitability beneath.
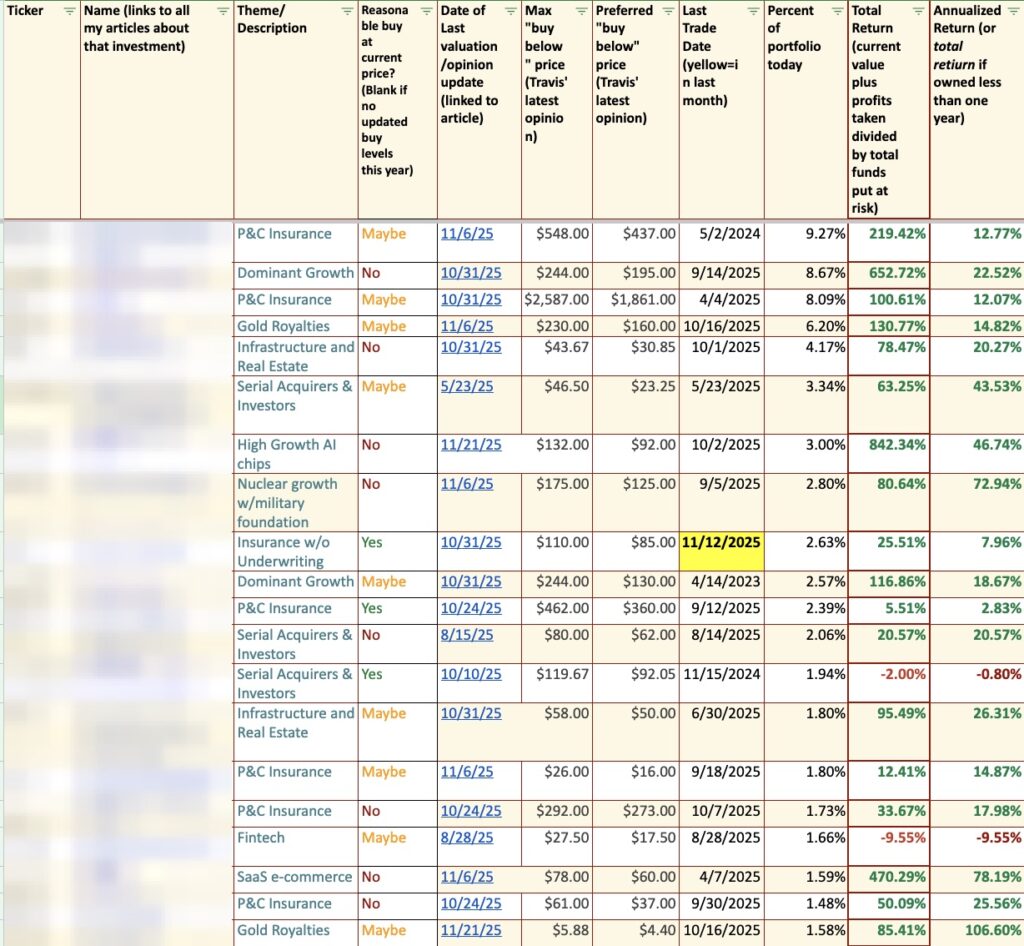
As we are able to see within the charts beneath, the credit score high quality of telecom firms took a success from 2005 till roughly 2021. Nonetheless, extra not too long ago, the rankings have largely stabilised. Explanations for this embody an improved aggressive atmosphere on account of new industrial methods round fibre upselling. Profitability and money era had been additionally aided by decrease curiosity prices, largely pushed by central financial institution insurance policies. However the financial atmosphere with ultra-low rates of interest was most likely a one-off, and there’s no certainty that value competitors stays at bay.
Our analysis exhibits that firms with (sturdy) funding grade rankings are properly positioned to climate headwinds, whereas high-yield firms could discover themselves cornered, particularly if they’ve bought their property.
Credit score rankings have stabilised
Supply: S&P rankings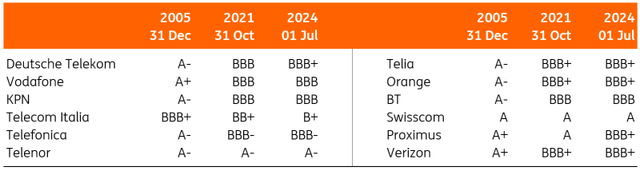
Robust funding grade firms can stand up to headwinds simply
Across the flip of the century, it was widespread for telecom firms to function with modest leverage and a robust single A ranking, reflecting glorious profitability, a robust steadiness sheet, wholesome money flows and, typically, authorities possession. This helped to mitigate the strain on the business that might play out in subsequent years. Regulatory motion has considerably decreased profitability within the sector for the reason that flip of the century. Most measures had been centered on rising competitors, however regulators have additionally regulated wholesale broadband entry and roaming tariffs. Furthermore, spectrum auctions have typically been costly, whereas typically permitting for brand spanking new operators to enter the market. These measures collectively have decreased the profitability of telecom operators.
On the similar time, investments in fibre networks and new cell applied sciences decreased free money movement as capital expenditures went up. Many incumbent operators see higher profitability from fibre-based mounted/mobile-coverged merchandise (bundles combining a set broadband and cell merchandise) however we see no giant improve in free money movement era. That is most likely brought on by a necessity for additional funding in mounted and fibre networks, as investments haven’t but been accomplished in lots of international locations.
Earlier than the regulatory motion, free money movement era was excessive for firms with comparatively low leverage, as proven within the determine beneath. For a single A-rated firm (second column), Free Money Stream might virtually be approximated by EBITDA-Capital expenditures given low curiosity prices (the place EBITDA is a measure of profitability and a proxy for working money movement era earlier than paid taxes). Money taxes had been one other notable expense line weighing on money flows.
This wholesome money era issues loads when EBITDA comes beneath strain, as we’ve got seen traditionally. We’ll present some examples beneath. Clearly, Free Money Flows are decrease when firms are extra indebted. This may be seen within the far proper column, for a BB-/B+ rated firm. The Free Money Stream-to-Debt ratio, particularly, is decrease for extra leveraged firms. A stable ratio issues if an organization desires to pay down debt from free money movement. That is obligatory when leverage must be stabilised within the occasion of an EBITDA decline. One might argue that free money movement yields enhance as soon as community upgrades are accomplished. Nonetheless, there’ll stay a notable distinction among the many very financially sound firms and telecom operators relying extra on debt funding.
Decrease rankings indicate weaker money flows (stylised instance)
Curiosity bills devour most FCF
Be aware that the indicated ranking additionally is dependent upon the power of the enterprise profile. Supply: ING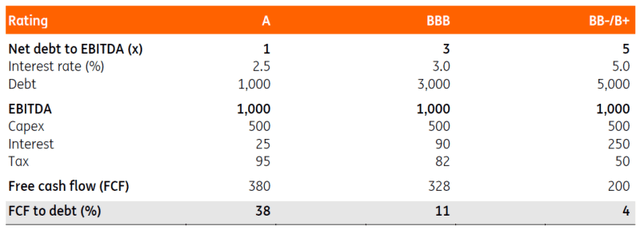
Corporations with a low ranking have much less meat on the bones
As illustrated within the stylised instance, firms with a decrease ranking have much less meat on the bones. Working profitability is similar. Nonetheless, the corporate generates much less money as a result of the upper indebtedness requires it to make bigger curiosity funds. Within the instance above, one sees that free money movement is €180 decrease (€380 versus €200) due to larger curiosity funds (balanced by considerably decrease taxes). When evaluating the free money flow-to-debt ratio, one sees that the power to scale back leverage from money flows is tougher. Whereas an A-rated firm might pay down all its debt inside three years, it takes for much longer for a BB-/B+ rated firm. Extra leveraged enterprise fashions are sometimes depending on EBITDA enlargement to scale back leverage. Nonetheless, when an business faces sturdy underlying headwinds, sturdy free money movement yields generally is a cornerstone for a corporation.
Materials declines in EBITDA do occur
The European telecom business is not the golden goose it was in my teenage years. Under, we’ll briefly present some examples of firms that confronted materials headwinds to EBITDA. We give attention to TDC and Telecom Italia. Previously, these firms suffered loads from regulation and fierce competitors. TDC reported a home decline in EBITDA of -12.7% in 2016 and -10.5% in 2015. Telecom Italia reported a home EBITDA decline of -9.8% in 2013, -9.6% in 2014, -20.6% in 2015 and -12.8% in 2021.
Outdoors Denmark and Italy, Altice France reported a -7.6% YoY EBITDA decline within the second quarter of this 12 months. Under, we’ll present how this impacts the leverage of firms. We deem it particularly fascinating to judge the affect from totally different levels of preliminary leverage. However it’s also a warning signal to telecom regulators that the telecom market wants to stay worthwhile. A spotlight solely on decrease client costs results in the break-up of telecom firms, finally.
Leverage will increase by 8% if EBITDA drops by -8%
Except money movement is used to decrease money owed
Supply: ING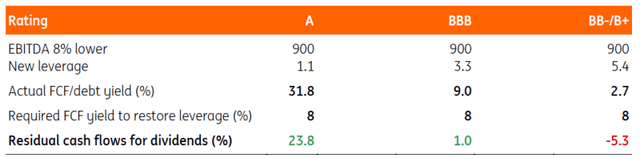
Indebted firms are challenged within the occasion of headwinds
Let’s analyse how firms with totally different levels of indebtedness are impacted by a considerable -8% EBITDA decline. Within the determine above, we offer some stylised figures once more.
On this desk, you could find the Free Money Stream-to-Debit ratio taken from the examples within the earlier determine. As mentioned beforehand, these ratios are a lot better for firms which have incurred low ranges of debt, with an A-rated firm having the ability to redeem c.32% of its money owed out of generated money flows (assuming there aren’t any dividend funds). For an organization with a BB-/B+ ranking, this ratio is barely 2.7% as a result of curiosity bills are larger. This issues loads when EBITDA declines, in our instance, by 8%. To stabilise the debt-to-EBITDA ratio on the stage earlier than the shock to EBITDA, money owed must lower by 8% as properly. As the instance above exhibits, this may be carried out inside a 12 months for firms with an FCF-to-Debt yield above 8% – firms with an A or BBB ranking. Nonetheless, for a corporation with an FCF-to-Debt ratio beneath 8%, leverage will improve following the drop in EBITDA from the instance.
In fact, one might make the evaluation considerably extra real looking by introducing dividend funds and longer time horizons to scale back debt. Nonetheless, we desire to maintain issues easy and simply need to present that there are materials variations within the capacity of firms to deal with steadiness sheet strain. We’ll briefly contact upon the potential of asset gross sales beneath. A powerful asset base – corresponding to possession of networks and towers – has at all times supplied consolation to lenders, because it acted as collateral.
Commerce-off return on fairness versus value of debt
On this article, we purposely don’t focus on the upper return on fairness derived from larger leverage as we need to clarify the debt lure firms could discover themselves in as soon as EBITDA comes beneath strain. It’s, nonetheless, easy that the price of debt rises with larger leverage. Ranking company S&P gives knowledge for the step-up in curiosity prices for company credit score issuers. Taking a look at current knowledge, credit score spreads improve by greater than 2% when companies go from an A- to a BB- ranking. This displays a double-digit share level improve in spreads for each notch downward from BBB+ to BB.
Debt maturities have been termed out
Regardless of the argument made above that dangers improve with larger debt ranges, we additionally like to notice that the affect of upper market rates of interest on the P&L happens slowly. That’s as a result of most firms within the TMT house have termed-out their debt profiles in the course of the period of low rates of interest. When wanting on the debt redemption profiles, one can see that the majority of maturities comes after 5 years. Be aware that one-year liabilities are sometimes substantial as a result of they may embody payables. Nonetheless, annual redemptions of senior debt are a fraction of the full excellent liabilities. Subsequently, the affect of upper funding prices will materialise slowly.
Debt maturities have been termed out
Supply: Corporations’ knowledge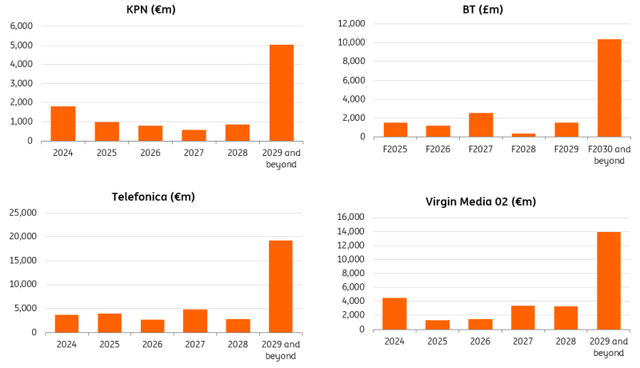
Different potential motion to enhance the steadiness sheet
In fact, different motion is feasible to revive steadiness sheets or improve free money movement. Money expenditures may very well be lowered to boost free money flows – though this isn’t good for community high quality and the aggressive place, and in flip, this measure due to this fact erodes the enterprise profile. In our instance, we’ve got already set the dividend to zero, however comparatively excessive dividends typically cut back the amount of money flows accessible for debt discount additional. The dividend payout ratio for telecom operators is a possible matter for a separate dialogue.
Lastly, asset gross sales was a part of the chance mitigation plan. Traditionally, traders took consolation from a robust asset gross sales base, the promoting of which may very well be used to shore up financials. Telefonica is an organization that has bought towers and (minority pursuits) in different property. Proceeds had been supposed to scale back indebtedness, with restricted success, as leverage stays excessive. A part of the reason is that firms that promote towers need to incur larger lease bills, lowering free money flows. Going ahead, we’ve got to see how asset-light enterprise fashions will fare. Telecom Italia not owns its mounted community, which might be an fascinating litmus take a look at.
For Altice France, leverage was an excessive amount of
Traders in Altice France had been spooked when the corporate introduced its intention to convey the proceeds from asset gross sales outdoors of their borrowing group. Whereas few traders doubt that leverage at Altice France is just too excessive proper now, our level is that different firms might discover themselves cornered as properly if sufficient consideration just isn’t paid to danger administration and monetary leverage. Stable financials are a robust argument for firms to favour a BBB+ or A- ranking, in our opinion.
Content material Disclaimer
This publication has been ready by ING solely for data functions regardless of a selected person’s means, monetary state of affairs or funding goals. The data doesn’t represent funding advice, and neither is it funding, authorized or tax recommendation or a proposal or solicitation to buy or promote any monetary instrument. Learn extra
Authentic Publish