Larger training programmes play a central function within the dissemination of up-to-date information, which is important for innovation and financial development (Jones 2005, Goldin and Katz 2010, Jones 2009). By their curricula, greater training programmes facilitate human capital accumulation and nurture future innovators, particularly in a world the place concepts have gotten tougher to search out (Bloom et al. 2017). But, these programmes have been proven to vary tremendously in scholar outcomes, together with earnings (Hoxby 2020, Mountjoy and Hickman 2020) and charges of invention (Bell et al. 2019).
We argue that greater training programmes have completely different talents to equip college students with up-to-date information. These variations are formed by traits on the faculty and teacher ranges, and so they can have necessary implications for labour market outcomes, training selections, and technological progress.
Novel information and strategies to measure the content material of upper training
In Biasi and Ma (2022), we convey collectively new information and a novel methodology to measure the extent to which greater training programs throughout US establishments cowl frontier – i.e. lately produced – information. Making use of fashionable textual content evaluation strategies to a big pattern in fact syllabi (capturing the content material of programs) and tutorial publications (capturing the frontier of data), we construct a novel metric – the training–innovation hole. The training–innovation hole is designed to seize the space between training content material and the information frontier. Particularly, we outline the hole because the ratio of similarities between a course’s content material and information from older vintages (lined by articles revealed a long time in the past) and between the course’s content material and new, frontier information (lined by the latest articles).
Naturally, the hole is greater for syllabi that cowl extra information that’s older (quite than newer). For instance, a pc science course that teaches Visible Fundamental (a comparatively out of date programming language) in 2020 would have a bigger hole than a course that teaches Julia (a more moderen programming language), as a result of Visible Fundamental is usually lined by outdated articles and Julia is usually lined by current articles.
Inspecting variations within the training–innovation hole throughout programs reveals stark variations within the protection of academic content material, each throughout and inside faculties. For instance, to maneuver a syllabus from the twenty fifth to the seventy fifth percentile of the hole distribution, roughly half of its content material must get replaced with newer information.
Instructors are essential in shaping course content material
Many of the noticed variation within the education-innovation hole (a couple of quarter) happens inside faculties, throughout programs taught by completely different instructors. The influence of instructors may also be seen from the truth that the hole of the standard course stays secure over time, however it declines considerably when the trainer of a course adjustments.
Determine 1 Occasion examine: The training–innovation hole round an teacher change
Notes: Occasion examine of the education-innovation hole round an teacher change, controlling for course and field-by-year mounted results. Observations are on the course-by-year stage; we give attention to programs with at most two episodes of teacher adjustments. Normal errors clustered on the course stage.
Most greater training instructors break up their effort and time between educating and analysis, reflecting the twin mission of universities to supply and disseminate information. As time is scarce, these duties are sometimes seen as competing (Hattie and Marsh 1996, Courant and Turner 2020). The character of upper training, although, may additionally create complementarities between the 2 (Becker and Kennedy 2005, Arnold 2008).
Our findings help the latter speculation: the training–innovation hole is considerably decrease for programs taught by instructors who’re extra energetic in producing analysis (i.e. they publish extra, are cited extra, and obtain extra grants). The hole is as an alternative greater for non-ladder school who concentrate on educating. The hole can be decrease when the trainer’s personal analysis is nearer to the subjects of the course.
These findings spotlight that correct deployment of school throughout programs can convey the content material of training nearer to the information frontier. In addition they recommend that investments in school analysis – each public (i.e. authorities grants) and made by every establishment – can generate further returns within the type of extra up to date instruction.
Important variations throughout faculties
Colleges clarify only a small fraction of the whole variance within the education-innovation hole. Nonetheless, cross-school variations are helpful for understanding how the content material of upper training is formed and the way the entry to frontier information varies throughout college students from completely different socioeconomic backgrounds. The hole is smaller in faculties with a stronger give attention to analysis (ranked as R1 within the Carnegie classification) and with extra sources (greater endowment and spending on instruction and analysis). The hole can be smaller in additional selective faculties (for instance the ‘Ivy Plus’, which incorporates the eight Ivy League schools plus Stanford, MIT, Duke, and the College of Chicago) in comparison with non-selective faculties. The magnitude of this distinction is such that to make the typical syllabus in a non-selective faculty corresponding to the typical syllabus in an Ivy Plus faculty, 8% of its content material must get replaced with newer information.
Determine 2 The training–innovation hole and college traits
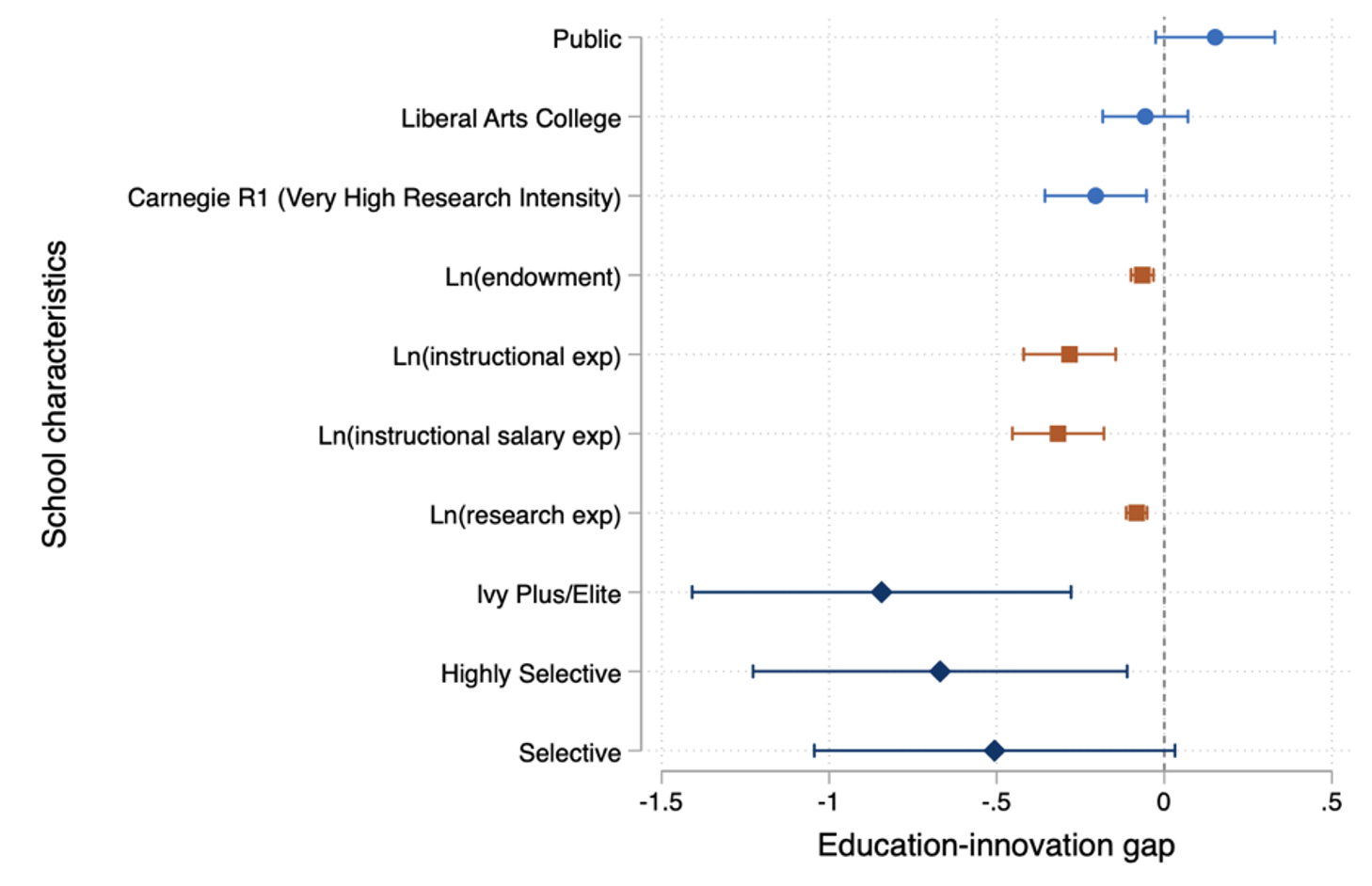
Notes: OLS level estimates and 95% confidence intervals of the slope of the connection between every reported variable and the education-innovation hole controlling for field-by-course level-by-year mounted results. Every estimate is obtained from a separate regression, apart from selectivity tiers (Ivy Plus/Elite, Extremely Selective, Selective), that are collectively estimated. Endowment, expenditure, and share minority discuss with the yr 2018 and are taken from Built-in Postsecondary Schooling Knowledge System. Estimates are obtained by pooling syllabi information for the years 1998 to 2018. Normal errors are clustered on the faculty stage.
Importantly, variations throughout faculties translate into disparities in entry to up-to-date information throughout college students with completely different backgrounds. The training–innovation hole is considerably greater in faculties enrolling college students with decrease median parental earnings and people with the next share of Black or Hispanic college students.
In precept, a part of these variations could possibly be as a consequence of a ‘vertical differentiation’ of academic content material throughout faculties. If college students with larger capability enrol in additional selective or better-funded faculties (Chetty et al. 2020) and are extra able to absorbing up-to-date content material, cross-school variations within the hole may merely replicate faculties’ efforts to offer college students with better-tailored academic content material. We don’t discover proof supporting this speculation: the unfavourable correlation between the hole and parental earnings stays once we management for scholar capability, through the use of the SAT and ACT scores of admitted college students.
Variations in course information content material are associated to college students’ outcomes
Do these variations matter for the manufacturing of innovation and college students’ outcomes? As scholar outcomes are usually obtainable on the aggregated faculty stage, we can’t examine the causal function of frontier information on these outcomes. We therefore decide on the extra modest, however nonetheless informative, objective of characterising the empirical relationship between the education-innovation hole and college students’ commencement charges, incomes, and measures of innovation, measured on the faculty stage. In an try and account for college kids’ choice into every faculty and different determinants of scholar outcomes associated to instruction, we management for a big set of college observables akin to institutional traits, expenditures, educational traits, enrolment by demographic group and main, selectivity, and parental background.
We discover that college students in faculties that provide programs with a decrease hole usually tend to full a doctoral diploma, produce extra patents, earn extra after commencement, and expertise greater intergenerational mobility (Chetty et al. 2014). They’re additionally extra more likely to graduate from school; a attainable clarification is that taking extra up-to-date programs makes college students extra motivated and thus extra more likely to full their training programme. Though our strategy is silent on what the ‘optimum’ education-innovation hole for a sure kind of college or college students ought to be, these correlations recommend that, on common, publicity to frontier information is related to higher scholar outcomes.
Course protection of sentimental abilities issues, too
Whereas the education-innovation hole measures the tutorial content material of every course, the richness of the data included within the syllabi permits us to transcend tutorial content material and discover the talents college students develop in every course. Latest works have highlighted the growing significance of sentimental abilities – non-cognitive attributes that form the way in which folks work together with others – for college kids’ success (Deming 2017, Deming and Kahn 2018). We measure the ‘soft-skills depth’ of every course because the extent to which evaluations are primarily based on actions that prepare gentle abilities, akin to group initiatives, shows, and surveys.
We discover that programs with a decrease education-innovation hole additionally are inclined to have the next soft-skills depth. Extra selective faculties, these with extra sources, and people serving extra socioeconomically advantaged college students train extra soft-skills intensive programs. Inside faculties, research-active instructors are probably to show soft-skills intensive programs. Lastly, soft-skills depth is strongly positively related to scholar outcomes.
Abstract and future analysis
The principle contribution of our work is to doc variations within the protection of frontier information throughout greater training programmes, a brand new and necessary dimension of heterogeneity throughout universities and instructors. Analysing the education-innovation hole, we shed new mild on among the most central questions associated to innovation and better training. Future work will shed additional mild on the function of instructors as each producers of data (within the type of analysis) and disseminators of it, and examine the causal hyperlink between the protection of frontier information in greater training and college students’ later life outcomes.
References
Arnold, I J M (2008), “Course stage and the connection between analysis productiveness and educating effectiveness”, Journal of Financial Schooling 39: 307–21.
Becker, W E, and P E Kennedy (2005), “Does educating improve analysis in economics?”, American Financial Overview 95: 172–76.
Bell, A, R Chetty, X Jaravel, N Petkova and J Van Reenen (2019), “Who turns into an inventor in America? The significance of publicity to innovation”, Quarterly Journal of Economics 134: 647–713.
Biasi, B, and S Ma (2022), “The education-innovation hole”, NBER Working Paper 29853.
Bloom, N, C Jones, J Van Reenen and M Webb (2017), “Concepts aren’t operating out, however they’re getting dearer to search out”, VoxEU.org, 20 September.
Chetty, R, J N Friedman, E Saez, N Turner and D Yagan (2020), “Revenue segregation and intergenerational mobility throughout schools within the US”, Quarterly Journal of Financials 135: 1567–633.
Chetty, R, N Hendren, P Kline and E Saez (2014), “The place is the land of alternative? Intergenerational mobility within the US”, VoxEU.org, 4 February.
Courant, P N, and S Turner (2020), “School deployment in analysis universities”, in Productiveness in Larger Schooling, College of Chicago Press.
Deming, D, and L B Kahn (2018), “Talent necessities throughout companies and labor markets: Proof from job postings for professionals”, Journal of Labor Economics 36: S337–S369.
Deming, D J (2017), “The rising significance of social abilities within the labor market”, Quarterly Journal of Economics 132: 1593–640.
Goldin, C D, and L F Katz (2010), The race between training and expertise, Harvard College Press.
Hattie, J, and H W Marsh (1996), “The connection between analysis and educating: A meta evaluation”, Overview of Academic Analysis 66: 507–42.
Hoxby, C M (2020), “The productiveness of US postsecondary establishments”, in Productiveness in Larger Schooling, College of Chicago Press.
Jones, B F (2009), “The burden of data and the loss of life of the renaissance man: Is innovation getting tougher?”, Overview of Financial Research 76: 283–317.
Jones, C I (2005), “Development and concepts”, in Handbook of Financial Development, Quantity 1, Elsevier.
Mountjoy, J, and B Hickman (2020), “The returns to varsity (s): Estimating value-added and match results in greater training”, College of Chicago, Becker Friedman Institute for Economics Working Paper.