Up to date on August twenty fifth, 2022 by Bob Ciura
This text covers 101 monetary ratios and metrics buyers must know.
This checklist is certainly not all inclusive. It does nonetheless comprise a number of attention-grabbing and informative metrics. You should utilize the hyperlinks under to immediately leap to a particular part of the article.
Desk of Contents
Metrics are listed by class under:
The 8 Guidelines of Dividend Investing are a compilation of among the most essential metrics on this checklist. The 8 Guidelines of Dividend Investing assist dividend progress buyers construct a portfolio of top quality dividend progress shares buying and selling at truthful or higher costs.
The Fundamentals – Revenue Assertion
The earnings assertion has (arguably) the one most essential monetary report in at this time’s enterprise world. It’s a good place to begin when analyzing a enterprise.
#1 Income
Income comes earlier than earnings. Income is also called gross sales or the ‘prime line’. It’s the sum of money generated from the sale of a services or products. If income is growing that exhibits an elevated demand for a corporation’s merchandise/companies. Declining income exhibits the alternative.
#2 Bills
Bills are the alternative aspect of income. Income much less bills equals revenue. Bills are all the prices a enterprise has (together with taxes, curiosity, payroll, analysis and improvement, value of products offered, and many others).
#3 Depreciation
Depreciation is the discount in worth of an asset over time attributable to regular put on and tear. For example, your automotive can be price much less subsequent yr than it’s price at this time. This lower in worth over time is expensed as depreciation in accounting. The depreciation of intangible belongings known as amortization.
#4 Earnings & Adjusted Earnings
You can not calculate the price-to-earnings ratio with out earnings. Earnings go by many names:
- Earnings
- Earnings
- The-bottom-line
- Web revenue
Earnings are what’s left over in spite of everything bills – together with curiosity and taxes – are paid.
Earnings are a GAAP measure (usually accepted accounting ideas). Firms will typically alter earnings for 1 time or uncommon bills. These might embrace lawsuits, restructuring prices, or acquisition prices.
When used accurately adjusted earnings present a firms ongoing earnings energy. Company managements will typically use adjusted earnings to cover actual issues within the enterprise. Each earnings and adjusted earnings ought to be scrutinized earlier than being blindly accepted.
#5 Earnings-Per-Share
Earnings-per-share is whole earnings dividend by whole share rely. It exhibits the quantity of revenue over the past 12 months that was generated for every share.
#6 Gross Margin
Gross margin is gross revenue divided by income. Gross revenue is income minus value of products offered. Gross margin tells you what proportion of income a enterprise retains earlier than paying any bills aside from the price of items.
#7 Working Margin
Working margin is working revenue divided by income. Working revenue consists of most bills, however doesn’t embrace curiosity or taxes. Working margin provides image of the profitability of a enterprise with out obscuring earnings energy with curiosity bills or variations in taxes.
#8 Web Margin
Web margin (additionally known as internet revenue margin) is internet earnings divided by income. It’s the ‘backside line’ quantity that exhibits what proportion of each greenback in income an organization retains after accounting for all bills.
The Fundamentals – Stability Sheet
The steadiness sheet exhibits the present place of a enterprise, together with money, debt, and belongings. It provides a snapshot of the monetary state of a enterprise.
#9 Belongings
An asset is property (together with intangible property) that has worth and will doubtless be used to satisfy money owed, commitments, or liabilities. Examples embrace present belongings, land, gear, goodwill, patents, and autos (amongst many others).
#10 Present Belongings
Present belongings are a subset of belongings. The definition of a present asset is any steadiness sheet merchandise that may be fairly anticipated to be transformed to money inside one yr. Examples embrace: money, money equivalents, marketable investments (like publicly traded shares), accounts receivable, and stock, amongst others.
#11 Liabilities
Liabilities are future obligations a enterprise is more likely to owe. They’re the alternative of belongings. Examples of liabilities embrace present liabilities and long-term debt.
#12 Present Liabilities
Present liabilities are the alternative of present belongings. Present liabilities are obligations which might be fairly anticipated to be paid inside one yr. Examples embrace short-term debt and accounts payable.
#13 Debt
The time period ‘debt’ is used interchangeably in accounting, finance, and investing. It typically refers particularly to bonds, credit score strains, and different borrowings. Sometimes debt is used as a synonym for liabilities, as is the case within the debt to fairness ratio.
#14 Fairness
Fairness is belongings minus liabilities. It’s a fast approach to broadly gauge the general constructed up worth in an organization. Typically, extra fairness is healthier than much less fairness. Fairness can be known as guide worth.
The Fundamentals – Money Circulation Assertion
The money circulate assertion exhibits money flows into and out of the corporate. It’s much less liable to administration manipulation than the earnings assertion.
#15 Capital Expenditures
Capital expenditures are cash spent by a enterprise to buy belongings. Capital expenditures are sometimes abbreviated as cap ex. You will need to differentiate between upkeep capital expenditures and progress capital expenditures. Upkeep capital expenditures ought to approximate depreciation (in straight ahead circumstances) over the long term. Progress capital expenditures are funds spent on increasing the enterprise moderately than changing previous parts of the enterprise.
#16 Working Money circulate & Money Circulation from Operations
Working money circulate (additionally known as money circulate from operations) is on the assertion of money flows, not the earnings assertion. Working money circulate exhibits an organization’s money flows from its regular operations. It doesn’t embrace depreciation and amortization, in addition to different non-cash prices.
#17 Free Money Circulation
Free money circulate is calculated as working money circulate minus capital expenditures. It’s a money based mostly measure that doesn’t undergo from the problems of accrual based mostly accounting. Many buyers desire free money circulate to earnings as ‘money doesn’t lie’.
The problem with free money circulate is figuring out the extent of upkeep capital expenditures to progress capital expenditures. Free money circulate can unnecessarily penalize companies that are investing closely in progress. Additionally it is extra variable from yr to yr than earnings.
The Fundamentals – Miscellaneous
#18 Market Capitalization
That is the whole market worth of an organization’s excellent shares. There are a couple of totally different courses of shares based mostly on market cap:
- Micro-caps: Market caps under $300 million
- Small-caps: Market caps of $300 million to $2 billion. See the Russell 2000 Shares right here.
- Mid-caps: Market caps of $2 billion to $10 billion.
- Giant-cap shares: Market caps of $10 billion to $200 billion.
- Mega-cap shares: Market caps above $200 billion.
#19 Enterprise Worth
Enterprise Worth calculates what it could value to fully take over a enterprise.
To take action you would need to purchase all of the shares in a enterprise (market cap) and extinguish all debt (whole debt). When you took over the enterprise you possibly can distribute all extra money to your self.
In its most elementary kind the components for calculating enterprise worth is:
Enterprise worth has been proven to be superior to market capitalization when rating shares based mostly on worth.
#20 Ticker
The ticker image (or ticker) is the 1 to five digit alphabetic code used to determine the shares of a particular company.
#21 Sector
Sector refers back to the broad enterprise class a inventory falls into. There is no such thing as a normal sector classification for various sectors. The most typical embrace the next:
Sector lists typically break shopper items into staples and discretionary classes. Vitality can be typically separated from primary supplies. Telecommunications can be typically given its personal sector.
It’s important to have some diversification between sectors when constructing your dividend progress portfolio.
#22 Quantity
Quantity is the quantity of shares of a inventory traded. It’s usually calculated as each day quantity. There may be extra danger with shopping for and promoting thinly traded shares because the bid-ask spreads are typically a lot larger. Increased quantity usually means it is possible for you to to purchase and promote simply.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios can be utilized to find out how environment friendly a enterprise is at earning profits. They’re additionally helpful in evaluating the profitability of various companies to 1 one other. Typically (and there are many exceptions – suppose Amazon for instance) larger profitability ratios imply an organization has a stronger aggressive benefit.
#23 Return on Belongings (abbreviated as ROA)
Return on Belongings is calculated as internet earnings divided by whole belongings. It is without doubt one of the easiest and simplest profitability ratios. Belongings are used to scale earnings as (nearly) each enterprise has belongings.
#24 Return on Fairness (abbreviated as ROE)
Return on fairness is calculated as internet earnings divided by fairness. It exhibits the share of revenue an organization could make on its fairness yearly. For some companies (a retailer in progress mode is an acceptable instance), it is a good approach to gauge how rapidly an organization can develop.
#25 Return on Invested Capital (abbreviated as ROIC)
Return on invested capital identifies the revenue an organization is making on cash from its capital base.
The numerator within the components is internet working revenue after taxes (abbreviated as NOPAT). This doesn’t embrace curiosity expense. The reason is that this ratio is trying to discover profitability earlier than cost to debt buyers.
The denominator within the components is invested capital. It’s calculated as whole belongings much less extra money and non-interest bearing present liabilities. The explanation extra money is subtracted is as a result of it’s not being utilized in actively funding the enterprise. Non-interest bearing present liabilities are subtracted as a result of they’re capital invested within the enterprise by suppliers, not buyers. That is principally ‘free capital’ and shouldn’t be included within the calculation. Accounts payable is an efficient instance of non-interest bearing present liabilities.
#26 Money Return on Invested Capital (abbreviated as CROIC)
CROIC is similar to return on invested capital. The denominator on this ratio is precisely the identical because the denominator in ROIC.
The distinction is within the numerator. ROIC makes use of NOPAT, whereas CROIC makes use of free money circulate within the numerator. Free money circulate is a money based mostly metric and is subsequently not topic to the various estimates that go into accrual based mostly measures like earnings.
#27 Gross Profitability Ratio
Robert Norvy-Marx’s paper titled The Different Facet of Worth: The Gross Profitability Premium discovered that companies with a better gross profitability ratio outperform these with a decrease gross profitability ratio.
Intuitively, this is smart. A enterprise that may earn excessive margins ought to have a robust aggressive benefit in place to have the ability to resist market forces and cost such a excessive premium. Extremely worthwhile companies ought to earn more money for shareholders than low profitability companies, all different issues being equal.
The gross profitability ratio may be very straightforward to calculate. It’s merely gross earnings divided by belongings. The upper the gross profitability ratio, the higher. It’s a fast approach to examine the quantity of gross earnings a enterprise can generate from its asset base.
Inventory Worth Threat Metrics
Investing danger is essentially a qualitative train. To essentially perceive the danger of a enterprise it’s essential to perceive its aggressive place out there and business.
Qualitative investing is very messy. When opinions are concerned there isn’t any proper or flawed earlier than the actual fact. This makes making a methodical framework for qualitative danger administration troublesome.
Maybe due to this, a number of inventory worth based mostly quantitative metrics have been designed to approximate investing danger.
#28 Normal Deviation
Inventory worth (return collection) normal deviation is probably the most generally used danger metric. It’s calculated because the annualized inventory worth normal deviation of a given safety.
Inventory worth volatility is used as a measure for danger as a result of companies with unsure futures ought to see their inventory worth fluctuate extra wildly (as prospects change on the drop of a hat) versus secure companies with safer futures.
#29 Beta
In most investing functions Beta refers to a particular securities’ sensitivity to general inventory market strikes. A Beta larger than 1 exhibits extra worth sensitivity. That’s to say, if the market declines by 10%, one would anticipate a inventory with a Beta over 1 to say no by greater than 10%. The converse is true on beneficial properties.
The upper the Beta, the riskier a inventory is assumed to be. It is because it’s extra delicate to the general market than a secure enterprise that isn’t so depending on being in a constructive market surroundings. You’ll be able to see a listing of excessive Beta shares right here.
#30 Most Drawdown
Most drawdown is the most important decline a inventory has suffered as measured from inventory worth excessive to inventory worth low.
Most drawdown is a helpful measure as a result of it exhibits the most important historic declines a inventory has suffered. If a inventory has historic most drawdowns of fifty% and an investor can’t tolerate most drawdowns larger than 25%, they haven’t any enterprise investing in that safety.
#31 Worth at Threat (abbreviated VaR)
Worth at Threat is used to calculate minimal potential loss at a given confidence interval. VaR usually makes use of historic returns and the conventional distribution. For example, you possibly can say on the 99% confidence interval (1% probability) my minimal anticipated loss is 20%. Mentioned one other method, I anticipate to lose 20% or extra of the worth of my funding 1% of the time.
Elementary Threat Formulation & Metrics
The ratios under take a unique method to quantitatively analyzing danger. As an alternative of taking a look at inventory worth motion, these formulation take information from a companies’ financials to quantitatively measure danger.
#32 Margin of Security
The margin of security idea is a danger administration methodology popularized by Benjamin Graham. When one finds their estimated truthful worth of an organization, they mustn’t pay truthful worth. As an alternative, require a margin of security in order that in case your truthful worth estimate is flawed, you continue to have margin of error in your buy worth.
Graham usually required a margin of security of 67%. If his truthful worth calculation was $10 per share, he would solely pay $6.70 for the inventory in order to take care of his margin of security.
#33 Sloan Ratio
A 1996 research (which has been up to date) by Richard Sloan on the College of Pennsylvania discovered that over a 40 yr interval (from 1962 by way of 2001) shopping for the bottom Sloan ratio shares and shorting the best Sloan ratio shares resulted in compound returns of 18% a yr.
The Sloan ratio components is proven under:

The Sloan ratio is used to see if reported internet earnings intently matches money flows. If it doesn’t, internet earnings might not precisely mirror enterprise outcomes.
- A Sloan ratio between -10% and 10% it’s within the secure zone.
- A Sloan ratio from -25% to -10% or 10% to 25% is within the warnings zone.
- A Sloan ratio lower than -25% or larger than 25% is the hazard zone.
#34 Piotroski F-Rating
The Piotroski F-Rating is an easy 9 level scoring system to separate profitable companies from unsuccessful companies.
The 9 level scoring system is damaged down into 3 classes:
Class 1: Profitability
- One level if constructive return on belongings in present yr
- One level if constructive working money circulate within the present yr
- One level if larger return on belongings in present yr than earlier yr
- One level if working money flows are larger than internet earnings in present yr
Class 2: Leverage, Liquidity, and Supply of Funds
- One level if long-term debt divided by belongings is decrease in present yr than earlier yr
- One level if present ratio is larger this yr than earlier yr
- One level if the corporate didn’t concern widespread shares within the present yr
Class 3: Working Effectivity
- One level if gross margin is larger in present yr than earlier yr
- One level if asset turnover ratio is larger in present yr than earlier yr
Investing in extremely ranked F-Rating shares and shorting lowly ranked F-Rating shares resulted in 23% annual returns from 1976 to 1996.
The F-Rating works by figuring out companies with money producing operations – which might be additionally seeing operations enhance.
#35 Altman-Z Rating
The Altman-Z Rating was first launched in 1968 by Edward Altman to estimate chapter danger for manufacturing corporations.
In 2012 he reintroduced the components and supplied an replace (known as the Altman-Z Plus Rating) for any sort of agency (not simply manufacturing issues). The components for the Altman-Z Plus Rating is under:
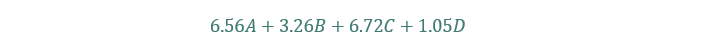
- A = Working Capital divided by Whole Belongings
- B = Retained Earnings divided by Whole Belongings
- C = EBIT divided by Whole Belongings
- D = E-book worth dividend by Whole Liabilities
If the Altman-Z Rating is above 2.6, the agency is probably going financially sound.
If the Altman-Z Rating is under 1.1, the agency is more likely to go bankrupt.
The typical Altman-Z Rating of non-bankrupt corporations is 7.7.
#36 Beneish-M Rating
The Beneish-M Rating is used to find out if an organization is manipulating its earnings. Catching earnings manipulators early can save buyers great sums of cash (probably the most well-known earnings manipulator is Enron).
The unique M-Rating consists of 8 variables. An up to date model consists of simply 5 variables however performs barely higher than the 8 variable model.
- Days gross sales in receivables Index (abbreviated as DSRI)
- Gross margin index (abbreviated as GMI)
- Asset high quality index (abbreviated as AQI)
- Gross sales progress index (abbreviated as SGI)
- Depreciation index (abbreviated as DEPI)
Every index metric is calculated as (Metric in present yr) divided by (metric in prior yr).
Every metric is given a corresponding weighting to calculate the Beneish-M Rating. The components is under:
![]()
If an organization’s rating is larger than -1.78 then there’s a excessive chance the corporate is manipulating its earnings. The extra unfavorable the rating, the higher.
Threat/Return Ratios
Analyzing efficiency based mostly upon returns alone doesn’t issue within the quantity of danger taken to accumulate these returns. The chance/return ratios under all take totally different approaches to higher quantifying funding efficiency whereas considering each danger and reward.
#37 Sharpe Ratio
Essentially the most broadly used danger/return ratio is the Sharpe ratio. The Sharpe ratio is proven within the picture under:

The Sharpe ratio subtracts the danger free charge of return from the return of the asset in query. This exhibits the extra return; the return above what you possibly can have comprised of investing in a ‘riskless’ asset. The riskless asset is often approximated through T-bill (quick time period United States authorities debt obligations with maturities lower than 1 yr) returns.
Associated: The Highest Sharpe Ratio Shares Inside The S&P 500
Extra return is then divided by the usual deviation of the return collection. This divides returns by a proxy for danger. The extra unstable returns are, the riskier they’re mentioned to be.
#38 Treynor Ratio
The Treynor ratio is similar to the Sharpe ratio besides it makes use of Beta as a substitute of normal deviation because the measure of danger.
The Treynor ratio is acceptable to make use of when a portfolio has diversified away non-systematic danger and has solely systematic danger remaining. An instance can be a well-diversified inventory mutual fund.
The components for the Treynor ratio is proven under:

#39 Sortino Ratio
The Sortino ratio seeks to enhance on the Sharpe ratio by higher defining danger. The Sortino ratio solely seems on the draw back normal deviation of returns. Which means that upside volatility (constructive returns) don’t impression danger.
That is logical in that the majority buyers are very blissful to see their shares leap 20% in in the future, regardless that this may improve the usual deviation of the return collection and improve danger in accordance with the Sharpe ratio. The Sortino ratio doesn’t undergo from this flaw.
The components for the Sortino ratio is under:

#40 Calmar Ratio & MAR Ratio
The Calmar & MAR Ratios are very related. They each makes use of Most Drawdown as the danger measure as a substitute of normal deviation. Each additionally don’t take the danger free charge of return under consideration.
The place the Calmar & MAR ratios differ is the time interval by which they calculate returns and most drawdowns.
The Calmar ratio makes use of 3 years of rolling information. The MAR ratio makes use of information since inception of the funding/portfolio/account.
The components for the Calmar Ratio is under:

The components for the Mar ratio is under:

#41 Sterling Ratio
The Sterling ratio is similar to each the Calmar and MAR ratios. The Sterling ratio takes under consideration the concept the largest historic drawdown will not be the most important attainable most drawdown.
The Sterling ratio has an arbitrary ‘+10%’ added to the most important most drawdown to account for probably bigger future drawdowns.
The components for the Sterling ratio is under:
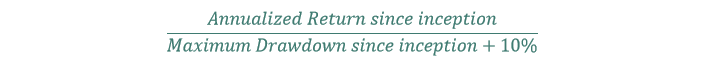
#42 Omega Ratio
The Omega ratio differs from the opposite ratios on this article.
To calculate the Omega ratio, one should first decide a goal return threshold. A standard goal is both 0% or the danger free charge (when calculating the Omega ratio).
The Omega ratio is calculated by summing historic returns above the return threshold minus threshold return and dividing them by absolutely the worth of the sum of returns under the brink minus threshold return.
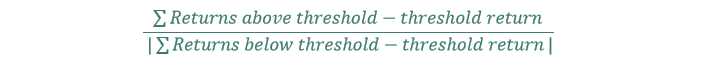
The Omega ratio can be utilized on non-normal distributions. This provides it a definite benefit over ratios that use normal deviation. Inventory worth returns approximate the conventional distribution, however they don’t seem to be really usually distributed. There are far too many ‘outlier occasions’ (suppose Black Monday in 1987) than a standard distribution would predict.
#43 Data Ratio
The knowledge ratio measures a portfolio’s consistency and returns relative to a benchmark.

A excessive info ratio is achieved by constructing a portfolio that:
- Carefully tracks an index
- Considerably outperforms an index
That is very troublesome. A excessive info ratio exhibits {that a} portfolio supervisor is sticking with the outlined technique whereas including important worth when making funding choices that differ from the index.
#44 Upside & Draw back Seize Ratios
The draw back seize ratio measures how a portfolio carried out versus a benchmark when the benchmark fell in worth.
The upside seize ratio measures how a portfolio carried out versus a benchmark when the benchmark rose in worth.
Seize ratios are calculated by dividing the portfolio efficiency over a time interval by the benchmark efficiency over the identical time interval.
In a perfect world your portfolio would seize the entire upside actions of the market and not one of the draw back actions.
Dividend Ratios & Metrics
There are a number of metrics suited particularly for dividend buyers. There are numerous causes to be a dividend investor. Chief amongst them is that dividend progress investing has traditionally outperformed the market – with decrease inventory worth normal deviation. Secondly, dividend progress investing offers rising dividend earnings over time, which is essential for buyers searching for regular earnings in retirement (or early retirement).
#45 Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is an organization’s dividend funds per share divided by its share worth. It is without doubt one of the most used metrics in dividend investing. All different issues being equal, the upper the higher. You’ll be able to see an in depth checklist of excessive dividend shares right here.
#46 Dividend Payout Ratio
The Dividend payout ratio is an organization’s dividends divided by earnings. The upper the payout ratio is the bigger the share of earnings getting used to fund the dividend. By definition a payout ratio above 100% is unsustainable.
#47 Dividend Payback Interval
The dividend payback interval calculates the variety of years it’s going to take a dividend progress inventory to ‘pay again’ the preliminary buy worth. The dividend payback interval may be calculated with:
- Inventory worth
- Anticipated progress charge
- Annual dividend cost
The decrease the dividend payback interval, the higher. The dividend payback interval will not be simply calculated like among the different metrics on this article (just like the P/E ratio, for instance). You’ll be able to obtain an Excel spreadsheet that rapidly calculates the dividend payback interval for a dividend progress inventory at this hyperlink.
#48 Yield on Value
Yield on value measures the % of dividend earnings your funding is producing from the acquisition worth.
In the event you purchase a inventory with a 3% dividend yield, after which annual dividend funds double over the following 10 years, your yield on value can be 6%.
Warren Buffett’s funding in Coca-Cola has a yield on value of round 50%. He’s getting again about 50% of his unique funding in Coca-Cola each yr from dividends.
Companies with robust aggressive benefits mixed with years of progress create massive yields on value.
#49 Dividend Low cost Mannequin
The components for the dividend low cost mannequin is proven under:

The dividend low cost mannequin is used to rapidly estimate the ‘truthful worth’ of a dividend progress inventory. An instance is under.
Think about an organization is anticipating $1.00 in dividends-per-share subsequent yr. The suitable low cost charge is 10%, and the expansion charge is 5%. This inventory’s truthful worth in accordance with the dividend low cost mannequin can be $20.
The fantastic thing about the dividend low cost mannequin is its simplicity. The problem in making use of it virtually is developing with a ‘truthful’ low cost charge and an correct future progress charge.
With that mentioned, the dividend low cost mannequin is a great tool for developing with a ‘ballpark estimate’ of truthful worth for dividend progress shares which have robust aggressive benefits.
#50 Dividend Historical past
Dividend historical past is just the period of time a enterprise has paid dividends. This will look like an arrogance metric, however dividend historical past issues.
Companies with 25+ years of rising dividends are much less more likely to minimize their dividend funds.
There are a number of attention-grabbing teams of shares by dividend historical past.
Progress, Return, & Efficiency Ratios & Metrics
Not sufficient buyers know in regards to the alternative ways of calculating progress. There’s a massive distinction between the arithmetic progress charge and the geometric progress charge
#51 Arithmetic Progress Price
The arithmetic progress charge is the easy common of returns. For example, let’s assume a inventory has the next returns over 3 years:
Below these assumptions the arithmetic common progress charge is 0% per yr. You would possibly suppose you got here out at break-even utilizing the arithmetic progress charge, however that isn’t the case…
In actuality your portfolio can be down 22%.
That is defined within the geometric progress charge part under.
#52 Geometric Progress Price
The geometric progress charge can be known as the compound progress charge or the time collection progress charge.
Keep in mind our instance from above? In the true world, compounding issues. The geometric progress charge takes under consideration compounding, additionally known as progress by way of time.
Think about you have got the next annual returns:
To calculate the geometric progress charge you’ll do the next:
![]()
This involves -7.9% a yr, which is a decidedly poor return (and never even near the 0% progress charge the arithmetic common would’ve calculated).
The components for utilizing the geometric progress charge is under:
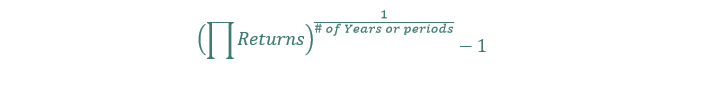
#53 Whole Return
Whole return is inventory worth appreciation (or depreciation) plus dividend funds. It’s the whole return from an funding, together with capital beneficial properties and dividends.
Whole return is usually used when calculating efficiency as dividends are sometimes a big portion of whole returns.
#54 Survivorship bias
Survivorship bias is a typical error in pondering and research. It’s once you look solely on the surviving shares in a research, and never on the ones that dropped out.
For example, when you have been to calculate the return of all Dividend Aristocrats since 2000 and solely regarded on the ones which might be nonetheless Dividend Aristocrats you’ll have survivorship bias in your research. It is because the research didn’t have in mind the shares that have been Dividend Aristocrats, however minimize their dividends between yr 2000 and now.
Valuation Ratios, Metrics, and Formulation
There is no such thing as a one ‘appropriate’ approach to worth a enterprise. There are nonetheless, all kinds of monetary ratios and metrics that can be utilized to check the relative worth of shares to 1 one other.
#55 Worth-To Earnings Ratio
The value-to-earnings ratio is without doubt one of the most essential investing metrics to know. It’s a fast approach to broadly gauge the sentiment round a inventory.
The upper the price-to-earnings ratio, the extra it’s essential to pay for $1 of an organization’s earnings. All different issues being equal, a excessive price-to-earnings ratio alerts the market expects speedy progress from an organization whereas a low price-to-earnings ratio alerts anticipated low or unfavorable progress.
At a price-to-earnings ratio of 20, it’s essential to pay $20 for each $1 of annual earnings from the corporate. The value-to-earnings ratio is calculated as share worth divided by earnings.
#56 Enterprise Worth to EBITDA
There may be important proof that the Enterprise Worth to EBITDA ratio is without doubt one of the two finest valuation metrics. It has traditionally outperformed the next metrics:
- Worth-to-earnings
- Enterprise worth to free money circulate
- Enterprise worth to gross revenue
- Worth-to-book
It seems that utilizing enterprise worth as a substitute of market cap (which is similar as worth) within the denominator of worth ratios improves outcomes. That is doubtless as a result of enterprise worth takes under consideration whole capital construction, together with debt and money. In its easiest kind, enterprise worth is calculated as follows:
Companies with massive quantities of money on their steadiness sheet and no debt rating higher with enterprise worth than they do with market capitalization.
Utilizing EBITDA can be helpful. EBITDA is probably the most effective measure of displaying how a lot money a enterprise is producing no matter capital construction, taxation, and depreciation.
The most important draw back to EBITDA is that it doesn’t account for depreciation. That is moderately troubling, as depreciation is an actual a part of money flows. Utilizing EBIT instead of EBITDA is preferable from a conceptual standpoint.
#57 Enterprise Worth to EBIT
Not solely is utilizing EBIT instead of EBITDA preferable from a conceptual standpoint, it’s also preferable from a historic return standpoint.
Within the guide Quantitative Worth, Tobias Carlisle and Wesley Grey display that the Enterprise Worth to EBIT a number of has outperformed the EBIDTA to Enterprise Worth a number of (and all different valuation metrics) from the interval 1964 to 2011.
For buyers searching for a single valuation metric, Enterprise Worth to EBIT is probably going the most effective.
#58 Enterprise Worth to Free Money Circulation
This metric is just like the 2 above. As an alternative of utilizing EBIT or EBITDA within the denominator, it makes use of free money circulate. Free money circulate comes from the assertion of money flows moderately than from the earnings assertion and is preferable when one believes an organization will not be accurately stating earnings. Money doesn’t lie.
#59 Worth to Gross sales
The value to gross sales metric makes use of the very first merchandise on the earnings assertion – gross sales. The benefit the value to gross sales ratio has over others is that it really works for nearly all companies. Not all companies are worthwhile, however almost all have gross sales.
The value to gross sales ratio helps to check companies that will not be worthwhile at the moment, or which might be experiencing a brief decline in revenue margins.
#60 Worth to E-book Worth
The value to guide ratio compares the value of a inventory to its guide worth. This ratio works effectively for companies that depend on belongings or fairness to supply money flows. It isn’t effectively fitted to franchises, and doesn’t work in any respect on companies with unfavorable fairness.
#61 Worth to Tangible E-book Worth
Tangible guide worth is guide worth minus intangible belongings and goodwill. It seems solely at ‘actual’ belongings and ignores goodwill and different intangibles. The value to tangible guide worth ratio can be utilized instead of the value to guide worth ratio when one feels that an organization’s intangible belongings are obscuring the true worth of belongings.
#62 Ahead Worth to Earnings Ratio
The ahead worth to earnings ratio divides the present worth by subsequent yr’s anticipated earnings. The ratio is beneficial when a enterprise’s present yr earnings are considerably understated or overstated by massive one time occasions.
#63 Worth to Earnings to Progress Ratio (abbreviated PEG)
The PEG ratio was popularized by Peter Lynch. It’s calculated as follows:

The PEG ratio takes under consideration progress charge when contemplating valuation. That is intuitive. An organization rising at 10% a yr ought to have a better price-to-earnings ratio than an organization rising at 2% a yr. The PEG ratio takes this under consideration.
A PEG ratio under one is usually mentioned to be a discount.
#64 Modified Worth to Earnings to Progress Ratio
The PEG ratio doesn’t have in mind dividend funds. Dividends generally is a massive a part of whole returns. The modified PEG ratio does take dividends into consideration.
The components for the modified PEG is under:

#65 Shiller Worth to Earnings Ratio
The Shiller worth to earnings ratio (additionally known as PE10) makes use of common earnings over the past 10 years as a substitute of trailing twelve months earnings within the denominator.
This method is helpful for cyclical companies or companies with quickly fluctuating earnings. This web site has a really long-term perspective on the S&P 500’s PE10 ratio.
#66 Destructive Enterprise Worth
In contrast to the previous valuation instruments, unfavorable enterprise worth will not be a ratio. A enterprise has a unfavorable enterprise worth when it has sufficient money on its books to fully repay all its debt AND purchase again all its shares.
This doesn’t (or very, very, not often) occurs to worthwhile companies. In the event you determine a enterprise with a unfavorable enterprise worth, it’s ripe for a takeover or acquisition. If the enterprise have been to be acquired, all of the money could possibly be distributed to shareholders and the enterprise be shut down, which might end in constructive returns with little or no danger.
You’ll be able to see a listing of unfavorable enterprise worth shares at this hyperlink. You should definitely examine information your self, and use a screener because the ‘first step’ within the investing course of. All the time do your due diligence.
#67 Low cost to Web Present Asset Worth
Web present asset worth is calculated as present belongings minus whole liabilities.
Web present asset worth is usually abbreviated as NCAV.
Benjamin Graham generated returns of round 20% a yr over a number of many years by investing in a diversified portfolio of corporations buying and selling at 67% or much less of their NCAV.
The concept behind NCAV is that if a enterprise is buying and selling for lower than the worth of its present belongings much less all liabilities, it is vitally definitely undervalued. Benjamin Graham wished a big margin of security (therefore the 67% of NCAV) on such a funding.
In at this time’s market, there are only a few NCAV shares accessible. NCAV shares turn into extra widespread throughout deep bear markets.
#68 Discounted Money Circulation
Discounted money circulate evaluation is a technique of discovering the ‘truthful worth’ of a enterprise. Discounted money circulate evaluation is the right approach to worth an funding in case you have 100% excellent info on the long run.
Discounted money circulate evaluation reductions the sum of all future money flows of a enterprise again to current worth utilizing an acceptable low cost charge.
Assuming you have got misplaced your crystal ball and your psychic powers have stopped working, discounted money circulate evaluation has critical flaws as a result of it requires so many assumptions.
Discounted money circulate evaluation requires the next assumptions:
- Low cost charge
- Progress charge
- When earnings stream will begin and cease
Due to this the truthful worth derived from discounted money circulate evaluation. With that mentioned, the metric does have utility in bringing to forth the assumptions you make in your valuation, and the way it results the whole worth of a shares.
#69 Earnings Yield
The earnings yield is the inverse of the price-to-earnings ratio. It exhibits what proportion of cash can be returned to you by an organization at a present worth when you owned the enterprise and distributed 100% of internet revenue.
#70 Magic System
The magic components was popularized by profitable Hedge Fund supervisor Joel Greenblatt in The Little E-book That Beats the Market.
The Magic System ranks shares on 2 metrics:
- Rank based mostly on EBIT/Enterprise Worth
- Rank based mostly on EBIT/(internet mounted belongings + working capital)
The primary rating sign within the magic components works very effectively. The second sign advertisements no worth and truly decreases returns from the primary sign as evidenced within the guide Quantitative Worth.
The concept behind the Magic System is to search out:
- Undervalued companies
- Companies with robust aggressive benefits
The EBIT/Enterprise Worth metric works effectively to search out undervalued companies.
The opposite metric (which Greenblatt refers to as Return on Capital) doesn’t work effectively in figuring out companies with robust and sturdy aggressive benefits.
Additionally it is essential to notice that Greenblatt’s claims of 30% annual returns from the magic components re disputed and can’t be independently verified by different historic research.
#71 Web Web Working Capital
Web Web Working Capital shares are enterprise buying and selling under liquidation worth. They’re extraordinarily low cost (and infrequently for good purpose).
When a enterprise trades for under liquidation worth, a bit of excellent news can ship the inventory surging upwards as it’s priced for nothing however negativity.
The components to calculate internet internet working capital (abbreviated as NNWC) is under:

Benjamin Graham created and popularized NNWC investing. NNWC capital shares are very uncommon in at this time’s investing world. NNWC shares have a tendency to supply very excessive returns over time (just like NCAV and Destructive Enterprise Worth shares).
NNWC investing is a type of deep worth investing.
#72 Shareholder Yield
Shareholder yield exhibits how a lot money an funding is returning to shareholders as in comparison with its worth.
Shareholder yield (in its most elementary kind) is calculated as:

Companies with excessive shareholder yields present that the corporate is:
- Buying and selling at a low worth relative to money returned to shareholders
- Has a shareholder pleasant administration that appears to reward shareholders with money
#73 Graham Quantity
Benjamin Graham pioneered worth investing. Consequently, most of the metrics within the valuation part come from him.
The Graham quantity seems to search out the utmost acceptable worth for a well-established enterprise. The Graham quantity is calculated as:

The Graham quantity finds the utmost truthful worth to pay for a enterprise. For example, if an organization has $1 in earnings-per-share and $5 in book-value-per-share, the Graham quantity can be $10.61. If the inventory was buying and selling for below $10.61 a share it could be a purchase (although Graham would doubtless search for a margin of security on prime of this).
Stability Sheet & Debt Threat Metrics
The last word danger dealing with any enterprise is insolvency. Having a excessive debt burden makes a enterprise going bankrupt extra doubtless as a result of it should continuously pay collectors. The metrics under take a wide range of approaches to taking a look at a companies’ means to deal with its debt burden.
#74 Fairness to Belongings Ratio
The fairness to belongings ratio exhibits the share of belongings owned by the corporate.
The components to calculate the fairness to belongings ratio is fairness divided by belongings.
The upper the fairness to belongings ratio, the larger proportion of the corporate’s belongings which might be owned by the corporate and never from debt purchases.
#75 Money Circulation to Debt Protection Ratio
This ratio is calculated as working money flows divided by whole debt.
The upper the ratio, the faster an organization can repay its money owed. If the ratio is above 1, the corporate may use its money flows to repay its debt in below a yr.
#76 Fast Ratio
The short ratio is used to find out an organization’s quick time period liquidity state of affairs.
It’s calculated as:

The short ratio is designed to point out if an organization is ready to meet its quick time period liabilities. If the short ratio is under 1, the corporate is at critical danger of chapter because it doesn’t have sufficient money readily available to pay money owed coming due within the subsequent yr.
The upper the short ratio, the higher.
The short ratio is also called the acid take a look at ratio.
#77 Debt to Fairness Ratio
The debt to fairness ratio is calculated as whole liabilities divided by fairness.
The ratio is used to calculate how leveraged an organization is relative to its owned worth (as measured by fairness).
Extremely leveraged companies are at larger danger of insolvency as they have to constantly meet their debt holder cost obligations.
#78 Curiosity Protection Ratio
The curiosity protection ratio is usually calculated as EBIT divided by curiosity expense.
The upper the curiosity protection ratio, the higher.
The curiosity protection ratio exhibits how effectively coated an organization’s curiosity bills are by its earnings earlier than curiosity and taxes.
Any enterprise with an curiosity protection ratio under 1 is in critical hazard.
An curiosity protection ratio above 1.5 is the brink for ‘not at fast danger’. Most secure companies have curiosity protection ratios far larger than 1.5.
Technical & Momentum Ratios and Indicators
The metrics under use inventory worth information to find out optimum entry and exit factors for investing.
#79 52-Week Vary
52 week vary is the excessive and low worth of a inventory over the past yr. For example, if a inventory had a excessive worth of $60 over the past yr and a low worth of $40 over the identical time interval, it’s 52 week vary can be $40 to $60 per share.
Momentum buyers usually look to purchase close to the 52 week excessive, whereas worth buyers can be extra thinking about shares buying and selling close to the 52 week low.
#80 Momentum
Momentum may be measured in a big number of methods. At its core it’s a measure of the previous efficiency of a inventory.
Optimistic momentum has been proven to supply market beating returns over the following month. The primary broadly credited massive research on the topic was performed by Jegadeesh and Titman in 1993.
Essentially the most broadly used measure of momentum is 12 month efficiency, skipping the latest month (11 months of efficiency information). It is because the primary month is related to imply reversion and is subsequently not included in momentum calculations.
Whereas momentum has been proven to supply extra returns on par with worth investing (and even outpacing it), momentum investing will not be appropriate for long-term buyers because it includes important shopping for and promoting (generally; there are momentum based mostly asset class methods with decrease turnover).
#81 Easy Shifting Common
The straightforward shifting common is a metric typically used to find out when an asset ought to be held, and when it ought to be offered.
The most typical easy shifting common used is the 200 day easy shifting common. Securities which might be buying and selling above their 200 day easy shifting common have been proven to have larger returns than when buying and selling under their 200 day easy shifting common. That is very doubtless the identical (or related) impact that’s picked up with previous efficiency momentum.
#82 Relative Energy Index (abbreviated RSI)
The relative power index compares current beneficial properties to current losses. The objective of the relative power index is to find out if a safety is overbought or oversold.
The components for the relative power index is under:
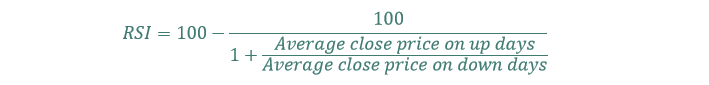
RSI ranges from 0 to 100. When the RSI is 70 or above the safety is alleged to be overbought. When the RSI is 30 or under it’s mentioned to be oversold.
#83 Common True Vary
Common true vary is usually abbreviated as ATR.
The typical true vary is one other approach to measure the volatility of a safety.
Common true vary is calculated as a easy shifting common (typically 14 days) of an organization’s true vary.
True vary is calculated because the highest of the next:
- Excessive in a interval minus low in a interval
- Absolute worth of interval excessive minus earlier shut
- Absolute worth of the interval low minus earlier shut
Capital Asset Pricing Mannequin & Portfolio Ratios & Metrics
The metrics under are utilized in fashionable portfolio principle and the capital asset pricing mannequin. As well as, metrics used to look at portfolio traits are included on this part.
#84 Alpha
Alpha is ‘extra return’. It’s return larger than what one would anticipate from an funding utilizing the capital asset pricing mannequin. Excessive constructive alpha exhibits one is outperforming the market whereas controlling for danger (as measured by Beta).
#85 Threat Free Price of Return
The chance-free charge of return is the return you possibly can generate from a ‘riskless asset’.
The time period is a little bit of a misnomer as no asset is actually danger free.
The proxy most frequently used for the danger free charge is the yield on Treasury Payments. The 1 yr treasury invoice at the moment has a yield of three.35%.
#86 WACC
WACC stand for weighted common value of capital.
The WACC exhibits the blended value of debt and fairness financing for a corporation. The components for WACC is under:
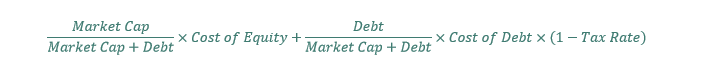
The price of fairness is the typical investor anticipated return from the widespread inventory. That is unknowable. In apply. The most typical approach to calculate the price of fairness is to make use of the capital asset pricing mannequin. The components for the capital asset pricing mannequin (abbreviated as CAPM) is under:
![]()
Instance:
- Threat free charge is 4%
- Anticipated market return is 9%
- Beta is 1.5
On this case, the inventory’s value of fairness is 11.5%.
Calculating the price of debt is simpler. The price of debt is the weighted common rate of interest on debt. Since rates of interest cut back taxes, a tax defend adjustment is made on the price of debt. That is the (1-Tax Price) portion of the WACC components.
Persevering with with our instance:
- Value of fairness is 11.5%
- Fairness financing is 60%
- Debt financing is 40%
- Value of debt is 8%
- Tax charge is 30%
On this case the WACC is 9.14%.
The WACC is beneficial in figuring out what tasks an organization ought to tackle. A enterprise ought to by no means tackle tasks with a projected charge of return under the WACC.
#87 R-Squared
R-squared is a measure of how effectively information suits a linear regression. R squared ranges from 0% to 100%. 100% is an ideal match, whereas 0% means your mannequin doesn’t clarify your information in any respect.
In investing R-squared measures how a lot of a fund or portfolios returns may be defined by underlying market motion.
#88 Energetic Share
Energetic share measures how totally different a fund or portfolio’s holdings are from the benchmark. The larger the distinction, the upper the energetic share.
Increased energetic share is considerably correlated with outperforming the market. One can’t hope to outperform a benchmark by a lot if energetic share is low, because the portfolio is simply too just like the benchmark.
#89 Monitoring Error
Monitoring error exhibits the distinction in efficiency between a fund or index and its benchmark. For ETFs, a big monitoring error is unfavorable as a result of the ETF will not be monitoring the benchmark it ought to be.
#90 Correlation
Correlation measures how securities transfer collectively.
Correlation ranges from -1 to 1. A rating of -1 is an ideal inverse relationship. A rating of 1 is ideal relationship; the securities transfer in lock-step with one another. A rating of 0 exhibits no relationship in any respect.
Investing in all kinds of securities with constructive anticipated returns and low correlations is the objective of a diversified portfolio. In apply, that is very troublesome as most asset courses see their correlations converge once you want them to not – throughout market corrections.
Various Earnings Metrics
Earnings will not be the one need to calculate cash ‘to the nice’ a enterprise generates. This part seems at a number of alternate options to earnings that buyers can use to trace how a lot cash an organization is making.
#91 Proprietor’s Earnings
Proprietor’s earnings is the earnings metric Warren Buffett makes use of. To calculate proprietor’s earnings, do the next:
- Begin with earnings
- Add again depreciation and amortization
- Add again non-cash prices
- Subtract upkeep capital expenditures
- If working capital elevated, subtract change in working capital
- If working capital decreased, add change in working capital
The troublesome a part of calculating proprietor’s earnings is discovering upkeep capital expenditures.
Upkeep capital expenditures are not a standard a part of monetary statements. Buyers should dissect capital expenditures and estimate how a lot was used for progress and the way a lot for upkeep.
#92 FFO
FFO stands for funds from operations.
This metric is usually used for REITs as a substitute of earnings. Since REIT’s belongings are their major enterprise, depreciation considerably impacts outcomes. Depreciation accounting guidelines typically don’t match up with actual world depreciation. This makes FFO obligatory.
FFO is calculated as internet earnings excluding beneficial properties or losses on the sale of property, with depreciation added again in. FFO is a significantly better profitability measure for REITs than earnings.
#93 AFFO
AFFO stands for Adjusted Funds From Operations.
It takes funds from operations and adjusts for recurring capital expenditures, in addition to different changes from administration. AFFO is usually probably the most consultant measure of ‘actual earnings’ from REITs.
Miscellaneous Descriptive Ratios & Metrics
#94 Quick Ratio
The quick ratio can be known as quick float. It exhibits the share of tradeable shares being offered quick. The upper the quick ratio, the extra buyers are betting a inventory’s worth will fall. Shares with excessive quick ratios are inclined to have critical questions concerning their underlying enterprise mannequin.
#95 Insider Possession
Insider possession is the share possession in a enterprise by the next:
- Shareholders with greater than 10% possession of the corporate
- Officers and administrators of the corporate
#96 Institutional Possession
Institutional possession is the share of possession of a inventory by massive ‘refined’ buyers corresponding to hedge funds, ETFs, mutual funds, personal fairness funds, and pension funds.
Giant institutional possession usually means a inventory can be effectively coated. On the draw back, excessive institutional possession can result in massive swings in a inventory’s worth as institutional buyers have a tendency to purchase and promote collectively.
Different Enterprise Efficiency Ratios & Metrics
#97 Money Conversion Cycle
The money conversion cycle is used to measure how rapidly an organization can convert money readily available into much more money readily available.
The money conversion cycle is damaged down into 3 elements:
- Days Gross sales of Stock (abbreviated as DSI)
- Days Gross sales Excellent (abbreviated as DSO)
- Days Payable Excellent (abbreviated as DPO)
The money conversion cycle is calculated as DSI + DSO – DPO.
#98 Days Gross sales of Stock
Days gross sales of stock measures the typical size of time an organization’s money is tied up in stock earlier than it’s offered.
Days gross sales of stock is calculated as:
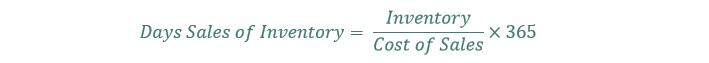
The decrease the times gross sales of stock is, the faster a enterprise can convert its stock into gross sales.
#99 Days Gross sales Excellent
Days gross sales excellent calculates how lengthy an organization takes to gather on its gross sales. Days gross sales excellent is calculated as:
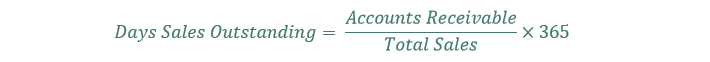
The decrease the times gross sales excellent is, the quicker an organization can gather on its funds.
#100 Days Payable Excellent
Days payable excellent measures how lengthy an organization can wait earlier than paying again its collectors. It’s calculated as follows:
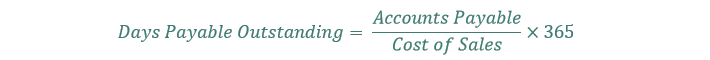
The upper the times payable excellent, the extra free credit score an organization can squeeze out of its provides.
#101 Stock Turnover Ratio
Stock turnover ratio exhibits what number of occasions in a single yr an organization’s stock is being changed. The upper the stock turnover ratio, the faster stock is ‘flying off the cabinets’, and (generally) the extra demanded an organization’s merchandise are.
The stock turnover ratio is calculated as gross sales divided by common stock in a interval.
Extra Studying
The next Certain Dividend articles comprise many high quality dividend shares:
Thanks for studying this text. Please ship any suggestions, corrections, or inquiries to [email protected].
















